Air is an invisible artist; it holds secret powers. Metals and non-metals react differently with air, revealing the secret of oxygen, which is quietly influencing the materials around us.
Let us learn the reactions of metals and non-metals with air. Observing these reactions helps us understand the unique properties of different materials.
Activity: Burning of magnesium ribbon
Materials required:
- Magnesium ribbon (\(2\) to \(3\) cm long)
- Two tongs
- Burner
- Two goggles
- Watch-glass
- Red and blue litmus papers
- Distilled water
- Beaker and sandpaper
Experimental procedure:
Step 1: Take a magnesium ribbon (2 to 3 cm long) and clean it with sandpaper. This cleaning will remove the oxide layer that has been placed on the magnesium ribbon, making it inactive.
Step 2: Hold the magnesium ribbon over a watch glass with tongs and burn it in the air using a burner (as shown in the figure). Using a pair of dark-coloured goggles, watch the burning magnesium ribbon.
Step 3: Take a watch glass and collect the white powder ashes.


Burning of magnesium ribbon
Observation:
- We observe that the magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame.
- The magnesium ribbon is converted into a white powder (collected in the watch glass).
Result:
The white powder collected after burning the magnesium ribbon is magnesium oxide (\(MgO\)).
Litmus test:
- Transfer the white powder to a beaker with a small amount of distilled water and mix it throughly.
- Pour a few drops of the mixture into the watch glass, and place the blue and red litmus paper on the watch glass.


Litmus test of magnesium oxide
Among the red and blue litmus papers, the colour of red litmus paper changes to blue. The colour of blue litmus paper remains the same (no change).
The difference in the colour of red litmus paper to blue suggests that the aqueous solution of magnesium oxide is basic in nature. Most metals react with oxygen, resulting in the formation of metal oxides. These metal oxides are basic in nature.
Metal + Oxygen \(\to\) Metal oxide
However, the reactivity of metals differs towards oxygen. It is based on the reactivity of the metals,
- Sodium and potassium react vigorously with oxygen.
- Magnesium and calcium brun slightly above the room temperature.


Reactivity series
- Iron does not burn when heated, but iron filings do when put into the burner's flame. Copper does not burn, but it does leave a black film of copper (II) oxide on the hot metal.
- Gold and platinum do not combine with oxygen even at high temperatures.
Metals like potassium and sodium react rapidly with oxygen and readily catche fire in the air. As a result, they are immersed in kerosene oil to protect them and prevent accidental fires.
Effect of air and water on non-metals
Activity: To find the chemical properties of non-metals
- Take a small quantity of sulphur powder in a spatula, and heat it by placing the sulphu powder over a burner.
- To collect the liberated gas, place an inverted test tube over the spatula.
- Carefully remove the test tube without allowing the gas to escape.
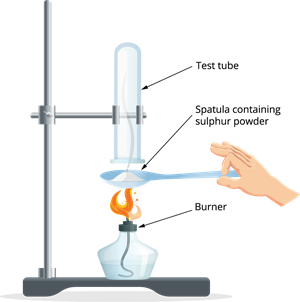

Burning sulphur powder on a spatula
Reaction:
On heating sulphur it leads to the formation of sulphur dioxide gas.
Litmus test:
Fill the test tube with distilled water and shake it. On a watch glass, add a few drops of the solution and place blue and red litmus paper on it.


Litmus test of sulphu dioxide
Among the red and blue litmus papers, the colour of the blue litmus paper changes to red. The colour of red litmus paper remains the same (no change).
The difference in the colour of blue litmus paper to red suggests that sulphur dioxide is acidic in nature.
Non-metals react with oxygen, resulting in the formation of non-metal oxides. Non-metal oxides are mostly acidic in nature.
Non-metal + Oxygen \(\to\) Non-metal oxide
Non-metals such as sulphur and phosphorus react rapidly with oxygen and readily catche fire in the air. As a result, they are stored in water to protect them and prevent accidental fires.
- Oxygen is essential for respiration, and it supports combustion.
- Sulphur is used for the manufacturing of gunpowder and the vulcaniastion of rubber.
- Phosphorus is used for making matches, rat poison, etc.
- Nitrogen is commonly used in the manufacturing of ammonia.
- Chlorine is used for sterilising water and as a bleaching agent for water purification.
- Hydrogen is used as rocket fuel.
- Diamond is used for making jewellery. Graphite is used for making pencil lead and electrodes (good conductor of electricity).
Reference:
https://th.bing.com/th/id/OIP.2q8wHQBtT6cTiWp7Lx6F6AAAAA?pid=ImgDet&rs=1
https://live.staticflickr.com/6091/6257265455_aed62037cc_b.jpg