Silver has a wide variety of uses in everyday life and is used in silverware and jewellery. Silver, when exposed to air for an extended period, turns black. This occurs when silver combines with sulphur in the air to form a silver sulphide coating.

Tarnishing of silver jewellery
Similarly, when copper reacts with moist carbon dioxide in the air, it loses its shiny brown surface and develops a green coating. This green substance is copper carbonate.
Rusting
The usage of iron and steel articles has become an integral part of our daily lives. People use iron for a wide range of daily life items, making bridges, ships, cars, truck bodies, grills in windows and many other articles.
Chemical reactions on the surface of shining metals and other items cause these articles to lose their shine. When iron is exposed to wet air for an extended period, it corrodes, forming a coating called rust, a brown, flaky substance.
Activity: Testing conditions in which iron objects develop rust
Take a few shining iron nails and place them in three different clean test tubes. Label them as test tubes 'A', 'B', and 'C'.
- In test tube \('A'\), pour enough water to partially immerse the iron nail, leaving some air space at the top of the test tube.
- In test tube \('B'\), pour enough clean water (without dissolved air) to completely immerse the iron nail. Then, add a layer of oil on top of the water to cover it.
- In test tube \('C'\), add some calcium chloride (a drying agent) and seal it tightly with a lid.
Place all three test tubes in a stable environment at room temperature, undisturbed.
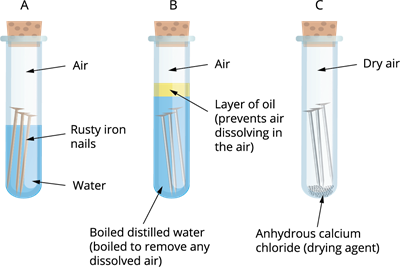
Testing iron nails in different conditions
Observation:
Iron nails rust in test tube \('A'\), but not in test tubes 'B' or 'C', as you will observe. The nails in test tube 'A' are exposed to both air and water. The nails in test tube 'B' are exposed to water only, whereas those in test tube 'C' are only exposed to dry air. Hence, rusting of iron requires both air and moisture.
Iron material loses its shine and turns into a red-brown flaky substance when exposed to air and moisture in the atmosphere for an extended period, a process known as rusting.
The chemical process of rusting is as follows,
\(Iron\) \(+\) \(Oxygen\) \(+\) \(Water\) \(\to\) \(Iron\) \(oxide\) (\(rust\))
\(4Fe + 3O_2 + xH_2O \to 2Fe_2O_3.xH_2O\)
Rusting occurs more rapidly in environments with high humidity (i.e., a high moisture content in the atmosphere) and a high salt content in the water.
Prevention of corrosion:
- Painting, oiling, greasing, chrome plating, and anodising can all be used to keep iron from rusting.
- Galvanisation is a process that coats steel and iron with a thin layer of zinc to prevent rusting. Even if the zinc covering on the galvanised item is broken, it remains protected against rusting.

Galvanised iron sheets
- Alloying is an excellent way to improve a metal's properties. This method can be used to obtain the desired properties. On combining iron with nickel and chromium, stainless steel is formed, which is hard and rust-resistant.
Some other metals also get corroded in this way. Have you ever observed the colour of the coating formed on copper and silver metals?
i. Copper, when exposed to moist air, undergoes corrosion and forms a greenish layer called patina (copper carbonate). The green coating is primarily due to copper reacting with carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)) and moisture (\(H_2O\)) in the air to form basic copper carbonate.
ii. Silver metal reacts with hydrogen sulphide gas present in the air to form silver sulphide. As a result, silver objects appear dull and black due to the layer of silver sulphide that is created on their surface.
Reaction of materials with water
i. Reaction of metals with water:
The reactivity of metals differs towards water. It is based on the reactivity of the metals,
- Sodium and potassium react vigorously with cold water, which liberates high heat during the reaction. The reaction is exothermic.
Sodium + Cold water \(\to\) Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas + Heat
- Calcium reacts with normal water to form calcium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Magnesium reacts with hot water to form magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Calcium + Normal water \(\to\) Calcium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas

Reactivity series
- Iron, aluminium, and zinc does not react with water, but when they come into contact with steam, they produce metal oxide and hydrogen.
Iron + Steam (water vapour) \(\to\) Iron oxide + Hydrogen gas
- Lead, copper, silver and gold do not react with water at all.
i. Reaction of non-metals with water:
Non-metals do not react with water, but they are reactive in air.
Non-metal + Water \(\to\) No reaction
Reference:
https://th.bing.com/th/id/OIP.2q8wHQBtT6cTiWp7Lx6F6AAAAA?pid=ImgDet&rs=1
https://live.staticflickr.com/6091/6257265455_aed62037cc_b.jpg