Imagine on a hot, sweltering summer day, you have decided to pull out some dark chocolate from the fridge. But as you leave it outside, it starts to transform. It appears to be melted when you remove it from the refrigerator.
Now, picture an ice cube that is cold and solid and sitting on a plate. Before your eyes, it begins to lose its form, slowly turning into a tiny pool of water.

Physical change - Melting of dark chocolate and an ice cube with water drops, and the ice is melting
But here's the magic part: if you take the melted chocolate or the water from the ice cube and return it to the freezer, it will revert to its original state. This fascinating transformation is a prime example of a physical change.
It’s all about shifting forms without creating anything new. Isn’t it amazing how easily we can witness these simple yet captivating changes in our everyday lives?
Also, assume that you have made dough with the wheat flour and prepared roti with it. Can you change it back into dough?
Likewise, if you burn a piece of paper, is it possible to recover it? No! That’s a chemical change. It is a change that cannot be reversed, resulting in the formation of a new substance.

Chemical change - Wheat flour to roti and burning a piece of paper
In this chapter, we will explore the physical and chemical changes that occur around us.
What is a change?
Change is a process in which a substance becomes a different one from what it was earlier. It is the difference between the initial and the final state of any substance.
The difference in the size or shape of an object is termed a 'change'. Change can be either reversible or irreversible.

Life cycle of a butterfly - Combination of both physical and chemical changes
Many changes are happening around us. Some occur slowly, some happen quickly; some can be reversed, while others cannot. Change is everywhere; all we need is the ability to observe and a curious mind to ask questions.
Let’s imagine entering the “Lab of Life”, where small experiments surround you!
A substance may change in appearance but remains the same:
With the help of a woollen yarn, you have knitted a sweater; in this scenario, you can get back the yarn while unknitting it, which can be reversed.
Any substance that changes its physical properties, such as size, shape, colour, or state, is known as a physical change.
Here, no new substance is formed. These changes are reversible; they can be brought back to their original form in nature.
Example:
i. Tearing a sheet of aluminium foil - Change in size.
ii. Melting an ice cube - Change in the state.
ii. Melting an ice cube - Change in the state.
Let us create and learn:
Creating some objects with paper: A paper plane is made by folding a sheet of paper. When unfolded, it comes to its original shape as before.
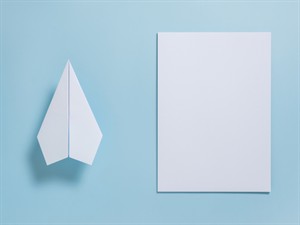
Making a paper plane
Playing with a balloon: When a balloon is inflated, it does not burst. As air is blown into the balloon, its shape and size change. When the air is released from the balloon, it returns to its original shape and size.

Inflated and deflated balloon
Primary aspects:
A physical change is like giving something a new look to, but deep inside, it remains the same.
- A physical reaction does not produce any new substances.
- Although usually reversible in many aspects, it may be a slow process or even irreversible, like breaking a glass object or cutting paper into pieces.
- The changes generally occur only in the physical properties, such as size, shape, colour and state. The changes are involved in the form, not in the substance identity.

Melting of ice cubes
The glass is filled with \(100g\) of ice cubes. When ice is melted, it gives \(100g\) of water. Here, physical change takes place with a state change. We call it a physical change because we can bring water back to the ice by freezing it.
A Substance may change in appearance and not remain same:
Green leaves can change to brown, crimson, or yellow in the autumn season. It's not merely drying up, it's a chemical change! A substance completely changes into something new. Chemical change alters something, preventing its return to the original form.

Transformation of leaf colours in the autumn season
Any substance that changes its chemical properties is known as chemical change. In this change, a new substance is formed, and these changes are irreversible (i.e. they cannot be brought back to their original form) in nature. These changes are permanent.
Example:
i. Bursting of a balloon
ii. Rusting of iron
iii. Burning of a matchstick
iv. Formation of curd from milk
ii. Rusting of iron
iii. Burning of a matchstick
iv. Formation of curd from milk
Bursting a balloon: If a balloon is blown to its full size and pricked with the pointed tip of a needle, it cannot regain its original form.

Bursting a balloon
Important!
Handle with care while using a needle.
Burning of a matchstick: When the matchstick is burned, it turns into ashes when it undergoes complete combustion. The ashes have an entirely new chemical composition from that of the unburnt matchstick.

Burining a matchstick
Do you like coffee? What is the process involved in making coffee?
When milk is combined with coffee decoction, the colour of the milk and decoction changes due to a chemical reaction. After that, you can add just the right amount of sugar to make it delicious.

Making coffee
Activity: To demonstrate a chemical change
Materials required:
- Glass tumblers
- Distilled water
- Lime water
- Straw
Instructions:
Step 1: Take two glass tumblers and label them as \(X\) and \(Y\). In the glass tumbler \(X\), fill with water and in \(Y\) fill with lime water.
Step 2: Use a separate straw for both the glass tumbler and blow air through the straw, and observe the changes.
Observation:
- Glass tumbler \(X\) - Due to the blowing of air, only bubbles arise in water, but there is no change in the appearance or colour of the water.
- Glass tumbler \(Y\) - Blowing air into the lime water, along with the bubbles, turns the lime water milky, which appears to be white.
Result:
In glass tumbler \(X\), there is no change. Whereas, in the glass tumbler \(Y\), when blowing air, the carbon dioxide gas passes into the lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of a new product, calcium carbonate.
The reaction can be given as,
Calcium hydroxide \(+\) Carbon dioxide \(\to\) Calcium carbonate \(+\) Water
The new substance is formed; it is a chemical change.
Primary aspects:
A chemical change is a kind of creation that changes the substance into a completely new one.
- A chemical reaction forms a new substance.
- Chemical changes are irreversible.
- There are several indicators of a chemical change, including a change in chemical properties, a colour change, the evolution of gas, and the absorption or release of heat or light during the reaction.