In the previous session, we learned about an indicator that allows us to understand the solution through colour changes. There is one more interesting factor, which indicates through smell, which is an olfactory indicator.
Olfactory Indicator:
The olfactory indicators are the substances which indicate a change in odour in acidic and basic media.
Example:
Onion, clove oil, garlic extract, and vanilla essence
When these substances are brought into contact with acids and bases, they convey the nature of the chemical, either becoming odourless or retaining the odour.
Activity - Testing solutions with an olfactory indicator:
Materials required:
- Onion and garlic
- Strips of clean cotton cloth
- Air-tight container
- Samples of acids and bases
Instructions:
Step 1: Take some garlic, finely chop it and add it to an airtight container.
Step 2: Add clean strips of cotton cloth to the same container, close it and leave it overnight.
Step 3: The next morning, remove the strips, and the strips smell like garlic.
Step 4: Now test the strips with acid and base samples. To one strip, add a few drops of lemon juice, and to the other strip, add a few drops of soap solution. Check the odour of the strips. Perform the same for onion.
Observation: In the acidic solution, the garlic-infused cloth strips retain the odour, while in the basic solution, they become odourless.
The observations are listed as follows,
|
Smell in acid
|
|---|
|
Retains odour
|
|
Retains odour
|
|
Retains odour
|
|
Retains odour
|
Acids:
The properties of acids are as follows:
-
Acids are sour.
-
The pH level of an acid is less than 7.
-
Litmus paper: It turns blue to red.
-
Acids release \(H^+\) ions, which are responsible for their acidic properties.

Properties of acid
Acids are commonly found in various fruits, including:
- Lemon contains citric acid.
- Oranges also rich in citric acid.
- Apple contains malic acid.
- Grapes have tartaric acid.
- Strawberry mainly contains citric acid and malic acid, with small amounts of ascorbic acid.
The acids that are present naturally are called organic acids, and acids which are synthesised in laboratories, like \(HCl\), \(HNO_3\) and \(H_2SO_4\), are mineral acids. Generally, organic acids are weak acids, whereas mineral acids are strong acids.
Strength of an acid:
- Strong acid: When complete ionisation of acids takes place in an aqueous solution, it is known as a strong acid. Here, the high concentration of \(H^+\) ions is present.
- Weak acid: When partial ionisation of acids takes place in an aqueous solution, it is known as a weak acid. Here, the low concentration of \(H^+\) ions is present.
Bases:
The properties of bases are as follows
- Bases are bitter, and they feel soapy or slippery.
- The pH level of a base is greater than 7.
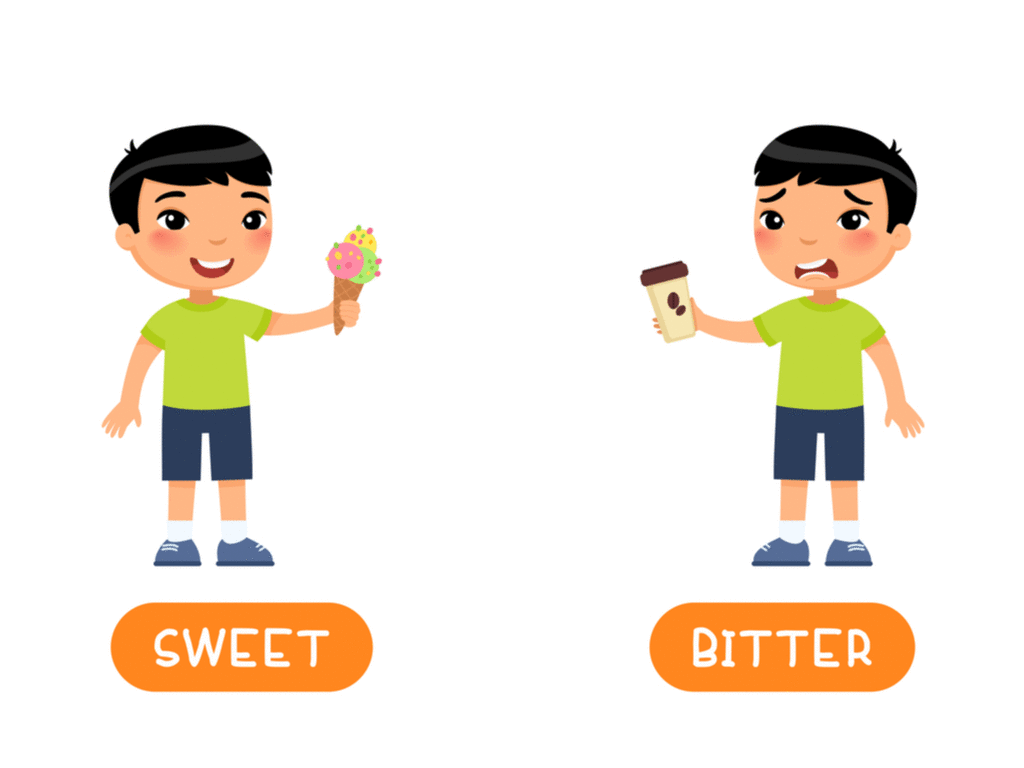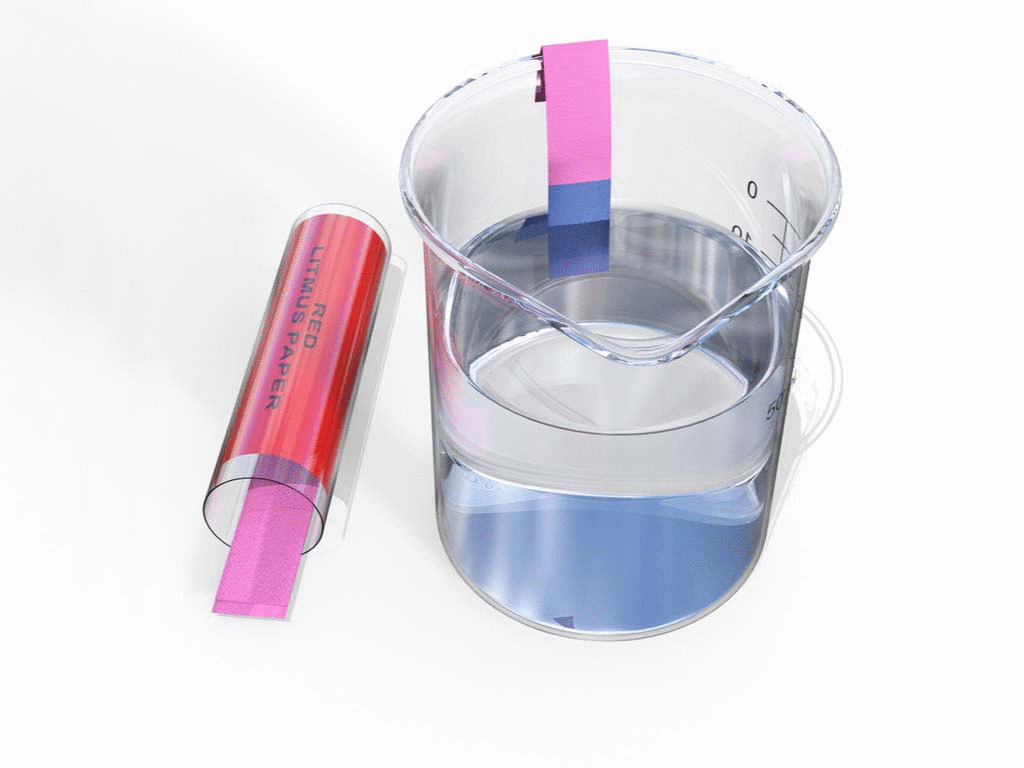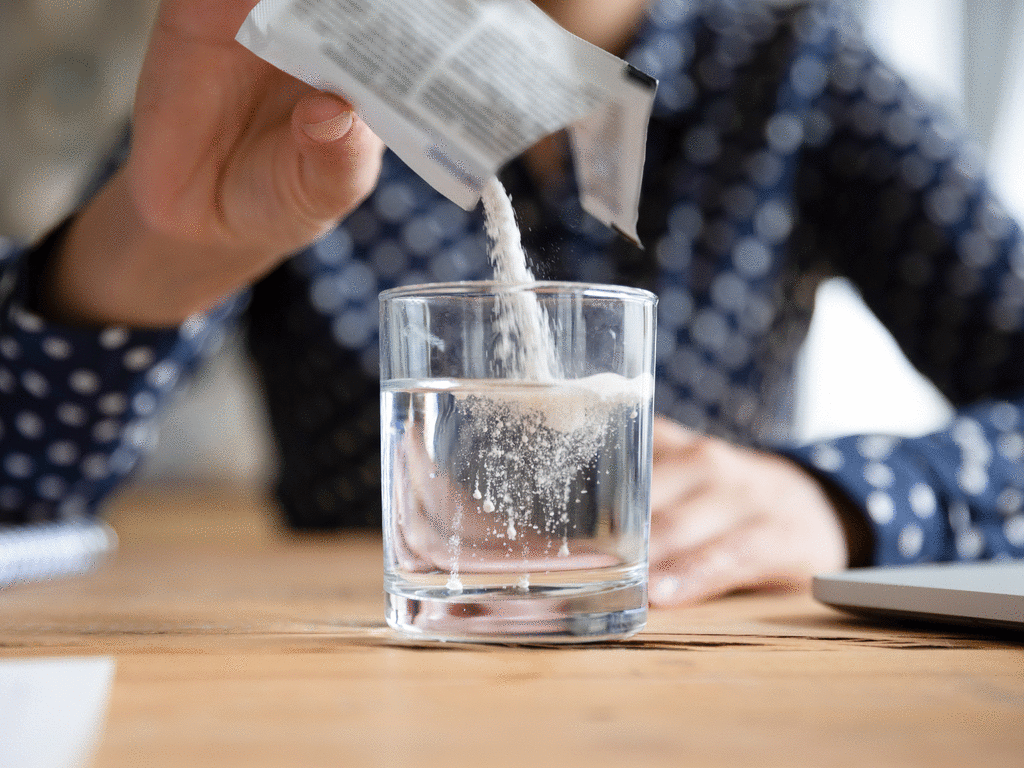
- Litmus paper: It turns red to blue.
- Bases that can dissolve in water are known as alkalis, for example, potassium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide.
- Bases release \(OH^-\) ions, which are responsible for their basic properties.
Properties of base
Bases commonly found in cleaning agents include:
- Soap is made using sodium hydroxide.
- Baking soda contains sodium bicarbonate.
- Cleaning products contains potassium hydroxide.
The organic bases are obtained naturally, like ammonia, urea, while inorganic bases are synthesised in laboratories like \(NaOH\), \(KOH\) and many more.
Strength of a base:
- Strong base: When complete ionisation of bases takes place in an aqueous solution, it is known as a strong base. Here, the high concentration of \(OH^−\) ions is present.
- Weak base: When partial ionisation of bases takes place in an aqueous solution, it is known as a weak base. Here, the low concentration of \(OH^−\) ions is present.
The classification of acids and bases based on their concentration:
i. Concentrated acid/base: If the aqueous solution contains a high percentage of acid/base and a low percentage of water, it is said to be concentrated acid/base.
ii. Diluted acid/base: If the aqueous solution contains a high percentage of water and a low percentage of acid/base, it is said to be diluted acid/base.
Neutralisation:
When two opposite characters meet, what happens? They don’t fight each other; instead, they shake hands and create peace. It’s like a coffee with a splash of milk, where the bitter black coffee meets the milk, which softens the bitterness, creating a delicious coffee.

Making coffee
When the angry acid comes in contact with the bitter base, they shake hands, resulting in the formation of peaceful droplets of water and salt, which enter the peacemaker- the neutralisation reaction.
When an acid and a base are combined, a chemical reaction occurs. This process is called neutralisation. The reaction mixture produces heat during neutralisation; hence, it is an exothermic reaction.
In a neutralisation reaction, there is the formation of a new substance, which is known as a salt. The salt produced as a product can be either acidic, basic or neutral.
Activity - Testing neutralisation of acid and base with litmus solution:
Instructions:
i. Take a small quantity of baking soda mixed with water in a clean test tube 'A', and add a few drops of red litmus solution.
ii. Observe the colour change, the red litmus solution changes to blue.
iii. To the same test tube, slowly add vinegar. At one point, the blue solution starts turning red as shown in 'B'.

Litmus test
Science behind it!
When a red litmus solution is added to the baking soda solution, it turns blue due to its basic nature. When vinegar was added to the same test tube, the colour of the solution changed from blue to red.
Thus, the solution in the test tube is no longer basic; vinegar neutralises the effect of the base.
The reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide yields a salt and water as products. It is one example of a neutralisation reaction.
Hydrochloric acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium chloride + Water + Heat
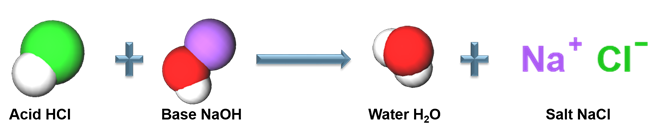
Acid-base reaction
Similarly, other acids also produce salt and water when reacting with the base. Let us see some examples of the reaction of acids with sodium hydroxide (\(NaOH\)).
Sulphuric acid + Sodium hydroxide → Sodium sulfate + water
Activity - Ready to inflate a balloon with the help of kitchen ingredients:
Materials Required:
-
Balloon
-
Plastic bottle
-
Spoon
-
Baking soda
-
Vinegar
Instructions:
Step 1: Fill half of the bottle with vinegar
Step 2: Add a tablespoon of baking soda into the uninflated balloon
Step 3: Carefully place the open end of the balloon over the bottle’s neck, without letting the baking soda into the bottle
Step 4: Gently lift the balloon so that the baking soda falls into the vinegar solution, and observe the reactionScience behind it!
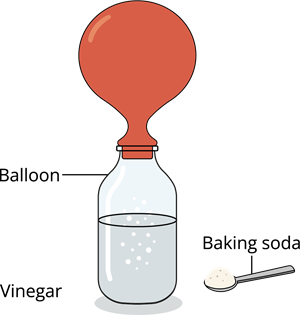
Baking soda reacts with vinegar
You might have observed that once the baking soda starts falling slowly, it mixes up and fizzes out, and the balloon begins inflating due to the release of carbon dioxide gas.
The following reaction occurs,
The acetic acid present in the vinegar, when it comes in contact with the base baking soda, leads to the formation of sodium acetate (salt), water, and carbon dioxide.
Neutralisation reaction in daily life:
Acid-base balance is pivotal for our health and the environment. We unknowingly perform many neutralisation processes in our daily lives. Let us now explore the significance of some of those reactions.
i. Acidity:
Scenario: Generally, our stomach secretes hydrochloric acid, which hates spicy foods and unhealthy junk. When Riya used to eat junk foods frequently, one day she got severe heartburn, causing burning and discomfort.
Acidity
Action Plan: Her mom gave her an Antacid. After some time, she was surprised that she was relieved of discomfort.
What Worked? Antacids are base that neutralise the excess acid in the stomach and lead to relief.
ii. Soil therapy:
Scenario: Have you ever noticed farmers apply fertiliser to enrich the soil? One day, the gardener saw that the plants didn’t seem healthy and there weren't many flowers blooming, so he checked the soil and found it was acidic.

Effect of pH on soil
Action Plan: He treated the soil with some lime, and slowly, the plants started to seem healthy and bloom.
What Worked? Since the soil is acidic, when it was treated with lime (\(CaO\)), which is a base, it neutralised the soil's condition and improved the soil's fertility.
iii. Insect bite:
Scenario: When Mokshitha was playing near the garden, suddenly she was bitten by something. She noticed that it was a bee. With stinging pain, she ran to her grandmother.

Effect of formic acid
Action Plan: Her grandmother immediately applied a paste to the skin where the bee bit. It was baking soda mixed with water, and in a few minutes, she felt relief from pain.
What worked? The bee sting injects formic acid into the skin, which causes pain as soon as it is applied. Baking soda paste, which is a base, neutralises the acid, and the pain fades away.
iv. Industrial waste balance:
Scenario: There was a factory in an area near a water body which released toxic acidic wastes. Harmful and corrosive, which affects the water as well as the environment.

Effect of industrial wastes
Action Plan: A team noticed it, and before letting the waste out, they passed it through a reactor tank, which contains base, and the waste which came out does not seem to be toxic.
What Worked? When the acidic waste is passed through a tank containing a base, it becomes neutralised, which renders the harmful waste harmless before releasing it into the water bodies.
Thanks to neutralisation, which serves as a solution to heartburn, provides relief from stinging aches, aids in soil therapy, treats acidic wastewater, and more.