When you look at a restaurant menu, you will notice that the dishes are not listed randomly; they are organised into categories like starters, main courses, desserts, and so on. Similarly, matter exists all around us in various forms.
Nature's menu card on the classification of matter can be organised into different categories:
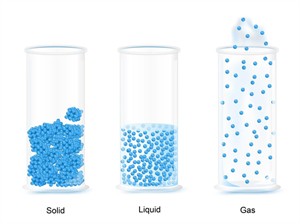
Based on physical state: Matter is classified as solid, liquid, or gas.

Classification based on physical state
Based on composition: Matter is classified as pure substances and impure substances.
Let us learn matter's classification based on their composition,
- Pure substance
- Impure substance or mixture
Matter
Matter is all around us. On the other hand, it can be defined as anything that has mass and occupies space. The air you are breathing is also a matter. The water we drink, the food we eat, the clothes we wear, and the air we breathe every day, each of these things has its own mass and volume.
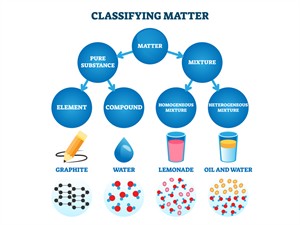
Classification of matters
i. Pure substance:
Pure substances are those that are completely made up of one form of particle. Physical processes cannot distinguish pure substances from other forms of matter.
The substances which are made up of only one kind of particle are known as pure substances. These are substances that cannot be separated into any other kinds of matter by any physical process.
Pure substances are further classified into elements and compounds.
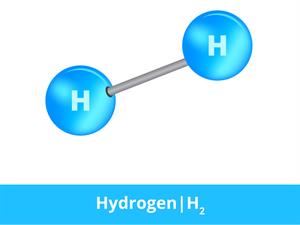
Hydrogen molecule
In hydrogen gas, the substance is made of the same atoms. Thus, two hydrogen atoms bond together to form a hydrogen molecule, which is in a gaseous state.
The other examples of pure substances are sugar, salt, diamond, etc. Crystals, in general, are known as pure substances.




Sugar and pure gold (\(24\) carat)
ii. Impure substances:
In a fruit salad, \(4\) to \(5\) kinds of fruits are mixed. It is an example of an impure substance, as we can separate them by the handpicking method into separate fruits.

Fruit salad
The combination of more than one kind of substance is known as an impure substance or mixture. A physical process can separate mixtures.

Lemon juice with honey and water
In fresh juice, fruit is mixed with water and sugar. There are three different kinds of substances present in it, so it is called a mixture.
A substance formed by chemical combination is called a compound, while a substance formed by a physical combination is called a mixture. Physical methods can separate a mixture.
Example:
Seawater, air, clay water, milk and cereals.
A mixture is a substance made of two or more elements or compounds or both, physically mixed in any ratio.
When you observe a glass of water, it may appear to be simple and ordinary at first glance. However, this clear liquid actually hides a fascinating partnership between two distinct gases: hydrogen and oxygen. How do we prove this? One effective method is through the process of 'electrolysis of water', which separates water into its elemental components.
Let us engage in an activity to learn and understand the nature of water as a compound and its elemental components.
Activity: Electrolysis of water
The process in which water is decomposed by passing electricity is called the electrolysis of water. When an electric current is used for decomposing a substance, it is called electrolysis.
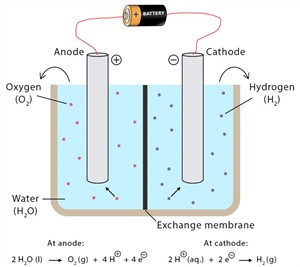
Electrolysis
Materials required:
- Plastic mug
- Rubber stopper
- Carbon electrodes (anode & cathode)
- Battery
- Water
- Dilute sulphuric acid and
- Test tube
Experimental procedure:
Step 1: Take the plastic mug and drill two holes at its base.
Step 2: Fit the two rubber stoppers in these holes.
Step 3: Insert the carbon electrodes (anode & cathode) into these rubber stoppers.
Step 4: Connect these carbon electrodes to a \(6\)-volt battery.
Step 5: Now, fill the plastic mug with water up to a level that allows the carbon electrodes to be immersed.
Step 6: Add a few drops of sulphuric acid to this water.
Step 7: Take two test tubes and fill them with water. Then, invert these test tubes over the carbon electrodes.
Step 8: Now, switch on the current from the \(6\)-volt battery.
Step 9: Leave the apparatus undisturbed for some time.
Observation:
- There will be the formation of bubbles at both electrodes in the test tubes (which means gas is forming or being liberated from the water)
- Due to the formation of bubbles, water begins to move in the test tube.
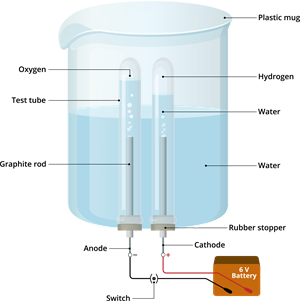
Electrolysis of water
Confirmation test of the liberated gases:
Once these test tubes are filled with the gases, carefully remove them from the mug. Take a glowing candle near the mouth of the test tubes to check which gas is present in them.
Important!
The teacher must carefully carry out this step.
Result:
- When we bring a glowing candle close to the mouth of one of the test tubes, the gas in the test tube takes fire and burns with a pop sound, showing the presence of hydrogen in the test tube.
- When we bring a burning candle closer to the mouth of another test tube, the candle starts to burn brightly, showing that the test tube contains oxygen.
- The gas collected at the anode (negative) is oxygen, and the gas collected at the cathode (positive) is hydrogen.
The volume of the gas obtained in both the test tubes is not the same. The volume of hydrogen gas is twice that of oxygen gas contained in the other test tube.
Decomposition reaction:
\(2H_2O\)(l) \(2H_2\)(g) + \(O_2\)(g)
Water Hydrogen + Oxygen
Conclusion:
In this reaction, water decomposes to form hydrogen and oxygen under suitable conditions. In this case, the electricity is a suitable condition under which the water gets decomposed. In the compound water, the hydrogen and oxygen are combined in a \(2:1\) ratio.
Fascinating combination of elements to create such a contrasting compound!
Hydrogen serves as an energy-rich fuel that can power various applications, while oxygen plays a crucial role in supporting combustion, allowing fires to burn brightly. Interestingly, when these two gases combine, they form water—a compound that acts as an effective fire extinguisher.

Firefighting with water
Reference:
https://www.chemistrylearner.com/electrolysis-of-water.html