Atomic mass:
One of the most significant ideas introduced by Dalton’s atomic theory was the concept of atomic mass.
The number of protons (\(p\)) in an atom is known as the atomic number (\(Z\)).
Mass number (A) = Number of protons + number of neutrons
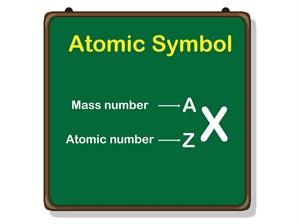
Atomic symbol
The atomic mass is expressed in grams or atomic mass units (amu). According to the new IUPAC guidelines, the atomic mass is written as 'u'.
Atomic masses of a few elements
While searching for various atomic mass units, scientists initially took \(1/16\) of the mass of an atom of naturally occurring oxygen as the unit. This was considered relevant due to two reasons:
- Oxygen reacted with a large number of elements and formed compounds.
- This atomic mass unit gave masses of most of the elements as whole numbers.
However, in 1961, for a universally accepted atomic mass unit, carbon-\(12\) isotope was chosen as the standard reference for measuring atomic masses.
One atomic mass unit is a mass unit equal to exactly one-twelfth (\(1/12\)th) the mass of one atom of carbon - \(12\).
The relative atomic masses of all elements have been found with respect to an atom of carbon-\(12\). The relative atomic mass of the atom of an element is defined as the average mass of the atom, as compared to \(1/12\)th the mass of one carbon-\(12\) atom.
Molecules:
Atoms of most elements are not able to exist independently. Atoms form molecules and ions.
- A molecule can be defined as the smallest particle of an element or a compound that is capable of independent existence and shows all the properties of that substance.
- A molecule is made up of two or more atoms chemically bonded together. These atoms may be of the same element or of different elements.
Examples:
- Water (\(H_2O\)): \(2\) Hydrogen atom + \(1\) oxygen atom
- Calcium oxide (\(CaO\)): \(1\) Calcium + \(1\) oxygen atom
- Glucose (\(C_6H_{12}O_6\)): \(6\) Carbon, \(12\) hydrogen, and \(6\) oxygen atoms
- Chlorine (\(Cl_2\)): \(2\) chlorine atoms
- Oxygen (\(O_2\)): \(2\) oxygen atoms
Molecules of elements:
Molecules made of the same-type atoms are called molecules of elements.
| Type | Example | Symbol | Atomicity |
| Metals | Copper | \(Cu\) | Monoatomic |
| Sodium | \(Na\) | Monoatomic | |
| Iron | \(Fe\) | Monoatomic | |
| Non-metals | Hydrogen | \(H_2\) | Diatomic |
| Oxygen | \(O_2\) | Diatomic | |
| Nitrogen | \(N_2\) | Diatomic | |
| Ozone | \(O_3\) | Triatomic | |
| Phosphorus | \(P_4\) | Tetra-atomic |
Atomicity: The number of atoms present in one molecule of an element.
Molecules of compounds:
When atoms of different elements combine chemically in a fixed ratio, they form molecules of compounds.
| Compound | Combining elements | Ratio by mass |
| Water (\(H_2O\)) | Hydrogen, Oxygen |
\(1 : 8\)
|
| Ammonia (\(NH_3\)) | Nitrogen, Hydrogen |
\(14 : 3\)
|
| Carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)) | Carbon, Oxygen |
\(3 : 8\)
|
Ions:
When a neutral atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes ions, which carry an electric charge.
- Cations: Positively charged ions formed by loss of electrons.
Example: \(Na → Na^+ + e^-\)
- Anions: Negatively charged ions formed by the gain of electrons.
Example: \(Cl + e^- → Cl\)
The process of forming ions by gaining or losing electrons is called ionisation.
Sodium chloride (\(NaCl\)) – Formed from \(Na^+\) (cation) and \(Cl^-\) (anion).
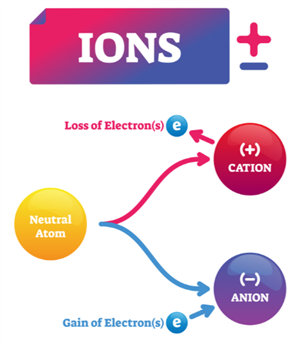
Ions
We understood how atoms combine to form molecules and ions. In the next session, we will learn how to write chemical formulae and find molecular masses of different compounds.