Generally, we know that matter occurs in three states such as solid, liquid and gas. Let us now classify matter based on their types.
- Pure substances
- Impure substances
Classification of Matters:
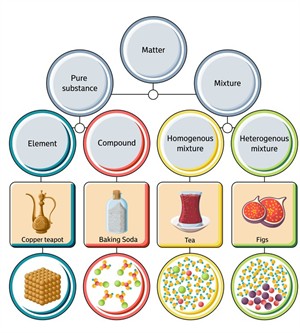
Classification of matters
Pure substance:
The substances which are made up of only one kind of particles are known as pure substances. These are substances that cannot be separated into any other kinds of matter by any physical process.
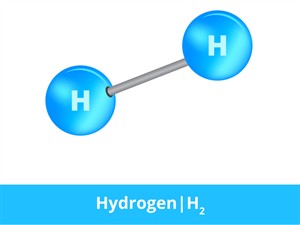
Hydrogen molecule
In hydrogen gas, the substance is made of the same atoms. Thus, two hydrogen atoms (\(H\)) bond together and form a hydrogen molecule (\(H_2\)) which is in a gaseous state.
Pure substances are those that are completely made up of one form of particle. Therefore, physical processes cannot distinguish pure substances from other forms of matter.
Example: Salt, sugar, and baking soda.
Based on the kind of atom, we classify pure substances as
- Elements
- Compounds
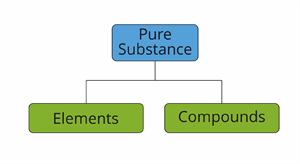
Classification pure substances
Elements:
Elements are the fundamental substances that cannot be separated into simpler substances by any chemical methods.
All the elements in the periodic table is an example for elements. In \(1661\), Robert Boyle became the first scientist to use the term 'element'.

Robert Boyle
Based on the physical and chemical properties, the elements are classified as,
- Metals
- Non-metals
- Metalloids
Properties of Metals:
1. Malleable (can be drawn into thin sheets)
2. Ductile (can be drawn into wires)
3. Lustre (shine) with silvery grey or golden yellow

Gold
4. Sonorous (capable of producing a deep or ringing sound when hit)
Example: Gold, copper, silver, iron, aluminium, and zinc
Properties of Non-Metals:
1. Non-metals come in a wide range of colours.

Non-metals
2. They are bad conductors of heat and electricity and are known as insulators.
3. They lack lustre, sonority, and malleability since they are brittle and soft in nature.
Example: Oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, and diamond
Properties of Metalloids:
- Substances that show the characteristics of both metals and non-metals are known as metalloids.
- There are around \(8\) elements in the periodic table that are called metalloids.
Example: Boron (B), Silicon (Si), Germanium (Ge), Arsenic (As), Antimony (Sb), Tellurium (Te), and Polonium (Po)
Note:
- Mercury (metal) and bromine (non-metal) are two elements that exist as liquids at room temperature.
- Diamond is a non-metal which is hard and lustre in nature.


Compounds:
It is a form of matter created by combining two or more elements in a specific mass ratio. To decompose it into its constituent components, we use chemical methods.
Example: Water\(H_2O\), oxygen \(O_2\), nitrogen dioxide \(NO_2\), salt \(NaCl\), and so on.
Impure substances:
The combination of more than one kind of substance is known as an impure substance or mixture. Mixtures can be separated by physical process.

Fruit salad
In a fruit salad, most of \(4\) to \(5\) kinds of fruits are mixed together. It is an example of a mixture, as we can separate them by handpicking method into separate fruits.
In fresh juice, fruit is mixed with water and sugar. There are three different kinds of substances present in it, so it is called a mixture.
The mixture is further classified into two types based on the property of substances they are made up of.
The mixture is further classified into two types based on the property of substances they are made up of.
Mixture:
A mixture is a substance made of two or more kinds of elements or compounds or both, physically mixed in.
Mixtures are classified into two types,
- Homegeneous mixture
- Heterogeneous mixture
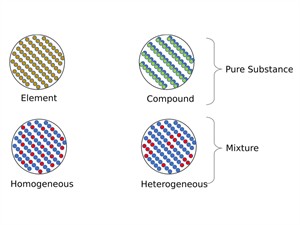
Arrangement in Mixtures
i. Homogeneous Mixture:
- All of the mixture's components are blended evenly.
- There are no visible separate barriers.
- There is just a single-phase solution.
- Salt in water is the best example.
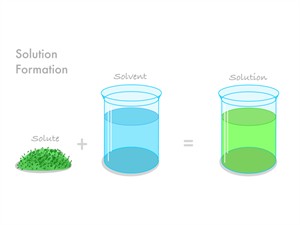
Homogeneous mixture
In a homogeneous mixture, components are cannot be seen through the naked eye. And it has a uniform composition and properties.
Example: Salt in water, sugar in water
ii. Heterogeneous Mixture:
- All of the mixture's components aren't evenly distributed.
- There are noticeable separate lines.
- There is two or more phase in the solution.
- Air, sand, and table salt are examples.
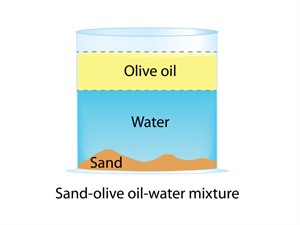
Heterogeneous mixture
In a heterogeneous mixture, components are visible to the naked eye. And it does not have a uniform composition and properties.
Example: Sand water, oil in water, chalk in water