Mixture:
A mixture is made up of one or more elements or compounds blended together rather than chemically combined.
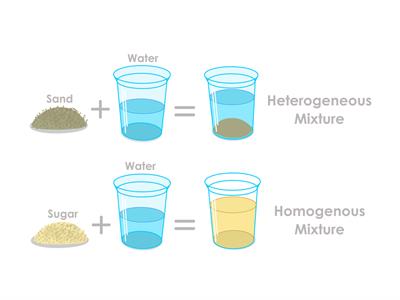
Types of Mixtures
- A mixture's constituents do not exist in a predetermined ratio.
- It is subject to change.
- In nature, mixtures can be either homogeneous or heterogeneous.
- Physical methods are used to distinguish mixture constituents.
- The constituents in a mixture retain their identities, i.e., a mixture displays all of the constituents' characteristics.
- Smog = smoke + fog. Therefore, it is an example of the mixture.
Compounds:
It is a form of matter created by combining two or more elements in a specific mass ratio. To decompose it into its constituent components, we use chemical methods.
Compound formation
- The elements in a compound are present in a fixed mass ratio, and this proportion will not change.
- Compounds are often homogeneous, meaning that their composition is consistent throughout.
- Physical methods cannot isolate the constituents of a compound.
- The constituents of a compound lose their identities, i.e., the compound loses its identity.
- Water \(H_2O\) is an example of a compound; as we chemically separate these elements, their properties differ from water.
Activity: Lets now see the difference between compounds and mixtures.
Step 1: Combine powdered iron filings and sulphur in a mixing bowl.
Step 2: Make two equal portions using the mixture.
Step 3: The first half of the mixture should be kept separately, while the second half should be heated.
Iron + sulphur \(\overset{Heating}{\rightarrow}\) Iron sulphide
Observation: When heated, a black brittle substance (iron sulphide) forms.
Result: The iron sulphide (compound) that forms has completely different characteristics than the iron and sulphur combination.
Iron sulphide \(=\) compound
Here when the magnetic field is applied, it has no effect.
Iron + sulphur \(=\) mixture

Magnetic effect on Iron and sulphur mixture
Here when the magnetic field is applied, the iron powder gets attracted.
Thus, from the above activity, we proved that the qualities of the elements of a mixture are displayed whereas the qualities of the individual elements are not visible in compounds.
Do you know why lemonade tastes the same throughout the drink?
Whenever we drink juice, it tastes the same throughout. This is because, it shows that particles of sugar or salt evenly distributed in the solution (juice).

Lemon Juice
Solutions:
A solution is a mixture of two or more substances that appears to be uniform in appearance. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances.
If we add the solvent and solute, we get the solution.
- A solute is a part of a solution that is present in a smaller quantity by weight.
- A solvent is a variable that is present in a greater quantity by weight.
Solution \(=\) Solvent \(+\) Solute.

Types of Solutions:
Various types of solutions are,
1. Solids in a liquid solution: Salt solution, sugar solution.
- Solute: Salt is the solute.
- Solvent: Water is the solvent.
2. Gas in a liquid solution: Aerated drinks.
- Solute: Carbon dioxide (gas) is the solute.
- Solvent: Water (liquid) is the solvent.
3. Solids in a solid solution: Alloys.
Alloys are mixtures of two or more metals, a metal and a non-metal, that can't be segregated into their constituent parts using physical methods.

Objects made from Brass
However, since an alloy exhibits its constituents' properties and may have a variable composition, it is still a mixture. Brass, for example, is made up of about \(30\%\) zinc and \(70\%\) copper.
4. Liquids in a liquid solution: Lemonade.
- Solute: Lemon extract is the solute.
- Solvent: Water is the solvent.
5. Gas in a gas solution: Natural gas, air.
Air is an example of a mixture in a gaseous solution. Air is a gaseous mixture that is homogeneous in composition.
Oxygen \(21\%\) and nitrogen \(78\%\) are the two primary constituents present in air. The other gases are only found in trace amounts. Natural gas is also an example of this type of gas in a gas solution.
Properties of solutions:
ii. Size of the particles: It is not possible to see the particles of a solution through naked eyes because these particles are smaller than in diameter.
iii. Scattering effect:
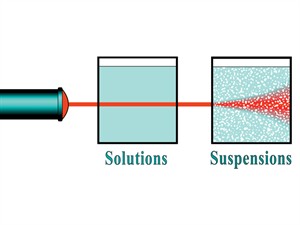
Scattering effect
The solution is a well-mixed homogeneous mixture, and the solution particles size is so tiny. So, we cannot see the light path when a beam of light passes in the solution. It is so because particles does not scatter light passing through the solution.
iv. Stable solution: In the filtration process, you cannot separate the solute particles from the mixtures because the solution is well mixed. As a result, the solute particles do not settle down even if it is left undisturbed.
The concentration of the solution:
Concentration is known as the ratio of solute in a solution to either solvent or total solution, and it refers to the amount of a substance per defined space.
Thus, the proportions of solute and solvent present in a solution determine the concentration of the solution.
a. Depending on the amount of solute in the solution, it may be called a dilute or concentrated solution.
1. Dilute solution: Dilute solution refers to a solution with a minimal volume of solute. This can also be known as an unsaturated solution.
2. Concentrated solution: A concentrated solution is a solution that contains a significant volume of solute.
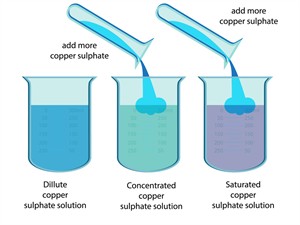
Concentration of solutions
b. Based on the dissolving limit of solvent and solute, the saturation can be classified into two types as a saturated solution and an unsaturated solution.
1. Saturated Solution: At a given temperature, a saturated solution is one in which no more solute can be dissolved.
2. Unsaturated solution: If the solution completely dissolves, leaving no substances remaining at the bottom is called an unsaturated solution.
Activity: Let us experiment to understand the saturated and unsaturated solution
Step 1: Take some water in a glass
Step 2: Add a small amount of sugar to that.
Step 1: Take some water in a glass
Step 2: Add a small amount of sugar to that.
We can observe that the sugar is dissolved completely. Now, add more and observe. Still, it dissolves well. This kind of entirely dissolved solution is called an unsaturated solution.
Now, add more sugar and heat the solution slowly.
Note: Remember that if the temperature is increased, then the dissolving power will also increase.
Observation:
But at a particular point, if you add more sugar, it stops dissolving and settles at the bottom of the glass, as the water attained its maximum dissolving limit known as saturation. Therefore, this kind of saturation is known as a saturated solution. Similarly, if we add more coffee powder to water, it will stay at the bottom without dissolving.