The Concentration of a Solution:
A solution is a mixture in which one substance dissolves fully in the other. The solute is the material that dissolves. The solvent is the substance that does not dissolve.

Solutions
A solution's concentration measures how much solute has dissolved in a given volume of solvent or solution. The concentrated solution is one in which the volume of dissolved solute is relatively high.
The formula below is used to calculate the concentration of a solution.
There are various ways to express the concentration of a solution, but here, we will learn these three well-known methods:
| \(\text{Concentration of solution}\) \(=\) \(\frac{\text{Amount of solute}} {\text{Amount of solvent or solution}}\) |
There are various ways to express the concentration of a solution, but here, we will learn these three well-known methods:
- Mass by mass percentage
- Mass by volume percentage
- Volume by volume percentage
1. Mass by mass percentage:
We can find the mass percentage of a solution by dividing the mass of solute by the mass of the solution and multiply the product by \(100\).
| Mass by mass percentage \(=\) \(\frac{\text{Mass of solute}}{\text{Mass of solution}}\) \(\times100\) |
2. Mass by volume percentage:
We can find the mass volume percentage of a solution by dividing the mass of solute by the volume of solution and multiply the product by \(100\).
| Mass by volume percentage \(=\) \(\frac{\text{Mass of solute}}{\text{Volume of solution}}\)\(\times100\) |
3. Volume by volume percentage:
|
Volume by volume percentage \(=\) \(\frac{\text{Volume of solute}}{\text{Volume of solution}}\)\(\times100\)
|
We can find the volume percentage of a solution by dividing the volume of solute by the volume of solution and multiply the product by \(100\).
Suspension solution:
In your childhood, you might have played in/with muds. But, have you ever gave a thought, what happens when we add mud to freshwater?
Will it dissolve or not?

Clay in water
We know that the soil or mud are in a solid-state, whereas water is in liquid-state. And, when you mix these two substances, mud or soil do not dissolve in the water. Therefore, this kind of solution is known as suspension.
The heterogeneous mixture in which the solute particles do not dissolve in the solvent and settle down entirely in the medium.
We can filter the undissolved particles by the filtration method. These particles are visible to the naked eye.
Example: Clay mixture with water, flour in water, and mixture of chalk and water.
Properties of a Suspension:
- Suspension is a heterogeneous mixture.
- The solute particle settles down when it is left undisturbed because suspensions are unstable.
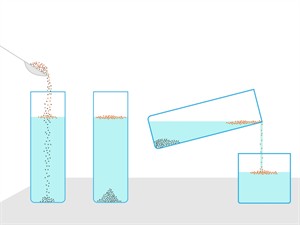
Solute particles settles down
- Through your naked eye, you can see these suspended particles.
- Suspension particles scatter a beam of light passing through it and make its path visible.
Note: When the suspended particles settle down, the beam of light is not scattered. We use filtration process to separate the suspended particles.
Colloidal Solution:
In everyday life, the products we use, such as mayonnaise, jelly, and butter are the colloidal solution.

Colloidal solutions
A colloidal solution is a heterogeneous mixture. In the colloidal solution, the particles of a colloid uniformly spread throughout the solution.
A colloidal solution contains finely divided particles (Approximately \(1\) to \(1000\) millimicrons in size), dispersed within a continuous medium in such a manner that prevents them from being filtered easily or settled rapidly.
Example: Milk, hair cream, toothpaste, fog, cheese, butter and paint
Properties of a Colloidal Solution:
- Colloidal solution is a heterogeneous mixture.
- A colloidal solution is quite stable so that it does not settle down when left undisturbed.
- Though the size of the particle here is so tiny, you cannot see with naked eyes.
- Colloidal particles can scatter a beam of light passing through it and make its path visible.
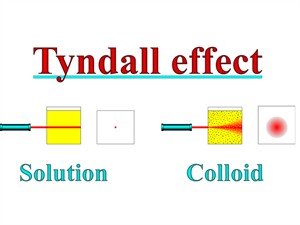
Tyndall effrct on colloids
Types of Colloidal Solutions:
Classification of colloids based on the physical state of the dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
a. Dispersed phase: The dispersed phase is described as a phase that is scattered or present in the form of colloidal particles.
b. Dispersed medium: The dispersed phase is the medium in which colloidal particles are distributed.
|
S.No
|
Name
|
Dispersed phase
|
Dispersed medium
|
Example
|
|
1.
|
Solid sol
|
Solid
|
Solid
|
Colored glass, Gems, Alloys.
|
|
2.
|
Sol
|
Solid
|
Liquid
|
Paint, Fruit jellies, Dye, Ink, Egg white
|
|
3.
|
Aerosol
|
Solid
|
Gas
|
Smoke
|
|
4.
|
Gel
|
Liquid
|
Solid
|
Cheese, Butter.
|
|
5.
|
Emulsion
|
Liquid
|
Liquid
|
Milk, Oil in water, Mayonnaise, Face cream.
|
|
6.
|
Aerosol
|
Liquid
|
Gas
|
Fog, Mist, Clouds, Body sprays.
|
|
7.
|
Foam
|
Gas
|
Liquid
|
Soap lather, Shaving cream, Coffee froth
|
|
8.
|
Solid foam
|
Gas
|
Solid
|
Rubber, Sponge, Cake, Bread
|