The distributive property is one of the most frequently used properties in mathematics. This property defines the relation between multiplication and addition, and is extensively used in arithmetic as well as algebraic simplifications.
The property states that when an integer or an expression is multiplied by a sum, the factor is multiplied to each term separately, and then the products are added.
For any three real numbers \(a\), \(b\) and \(c\)
- \(a(b +c) = ab + ac\)
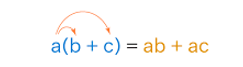
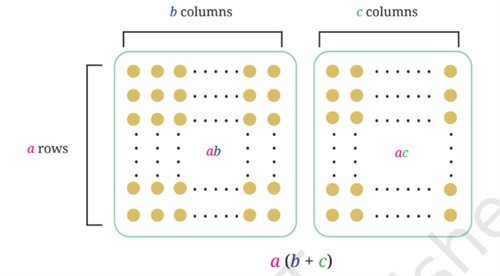
This property is visually representated using the following diagram:
We can also find the product of \((a + b)c\) using the distributive property as follows:
\((a + b)c\) \(=\) \(c(a + b)\) [By commutative property of multiplication]
\(=\) \(ca + cb\) [By distributive property]
\(=\) \(ac + bc\) [By commutative property of multiplication]
- \((a + b)c\) \(=\) \(ac + bc\)
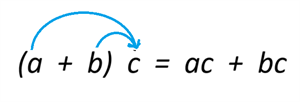
Example:
1. \(2 × (3 + 4)\) \(=\) \((2 × 3) + (2 × 4)\)
\(2 × 7\) \(=\) \(6 + 8\)
\(14\) \(=\) \(14\)
2. \(2 × (3 − 4)\) \(=\) \((2×3) − (2×4)\)
\(2 × (−1)\) \(=\) \(6 − 8\)
\(−2\) \(=\) \(−2\)
Important!
The real numbers can be either a negative integer or a positive integer or even can be replaced by an algebraic expression.