General expression for \((a+b)(a-b)\):
\((a+b)(a-b)\) \(=\) \((a+b)a - (a+b)b\)
\(=\) \(a^2 + ba - ab -b^2\)
\(=\) \(a^2 + ab - ab -b^2\) [Since \(ba = ab\)]
\(=\) \(a^2 - b^2\)
Therefore, \((a+b)(a-b)\) \(=\) \(a^2 - b^2\).
Identity :
Geometrical proof of identity:
Now, we construct a figure to understand the concept.
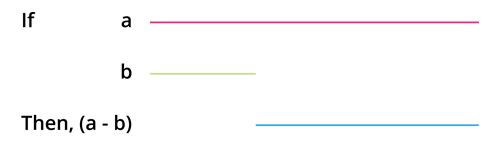
Then we construct a rectangle using the above information.
In the given figure, \(AB = AD = a\).
So, the area of square \(ABCD = a^2\).
So, the area of square \(ABCD = a^2\).
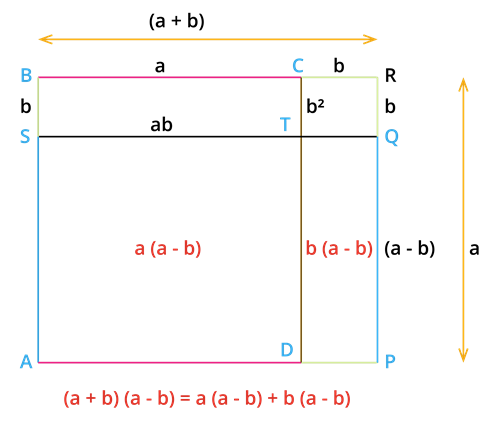
Also, \(SB = DP = b\). Then the area of the rectangle \(SBCT = ab\).
Similarly, the area of the rectangle \(DPRC = ab\). And, the area of the square \(TQRC = b^2\).
Area of the rectangle \(DPQT = ab − b^2\).
Hence, \(\text{the area of the rectangle APQS = The area of square ABCD}\) \(\text{– area of rectangle STCB}\) \(\text{+ area of rectangle DPQT}\).
Therefore, .
Example:
Simplify using the identity.
First, develop the given expression using the identity .
Here, \(a = 5x\); \(b = 9y\).
Therefore, \(=\) 25\(x^2 -\)81.