Fundamental Definitions:
Circle: A closed 2D figure consisting of all points equidistant from a fixed point (centre) in a plane.
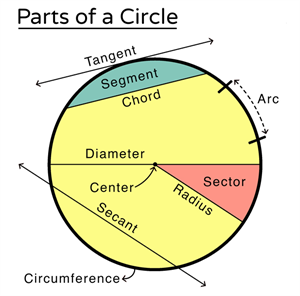
Radius: The fixed distance from the centre to any point on the circle.
Circumference: The boundary line or perimeter of the circle.
Interior/Exterior: A point is inside if its distance from the centre \(< \) radius, on the circle if distance \(=\) radius, and outside if distance \(>\) radius.
Lines and Segments
Chord: A line segment with both endpoints on the circle.
Diameter: A chord passing through the centre; it is the largest chord, twice the radius, and a line of symmetry that bisects the circle.
Secant: A line that intersects the circle at two distinct points.
Arcs and Regions
Arc: A portion of the circumference. Minor arc is shorter; Major arc is longer.
Semicircle: It occurs when the arc ends meet a diameter.
Segment: The region enclosed by a chord and an arc (Minor vs. Major).
Sector: The region enclosed by two radii and an arc (Minor vs. Major).
Congruent Arcs: Arcs that subtend the same angle at the centre.
Circle Types
Concentric Circles: Circles with a common centre but different radii.
Congruent Circles: Two or more circles with the same radius.
Points and Constructability
One/Two Points: Infinitely many circles can be drawn through a single point or a pair of points.
Three Points:
Collinear (on the same line): Zero circles can be drawn through them.
Non-collinear: Exactly one unique circle can be drawn through them.
Non-collinear: Exactly one unique circle can be drawn through them.
Reference:
https://pixy.org/5939397/
https://pixy.org/4801720/