Basics of Triangle Measurement:
The sum of all three sides of a triangle.
Standard Area Formula: Used when the base and height are known as
\(\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{Base} \times \text{Height}\).
Heron's Formula:
Named after the mathematician Heron (or Hero), this formula calculates the area of a triangle when only the lengths of the three sides (\(a, b, and c\)) are known. It is especially useful for scalene triangles where the height is not easily found.
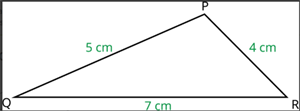
Calculate the Semi-perimeter \((s)\): \(s = \frac{a + b + c}{2}\).
Calculate the Area: \(\text{Area} = \sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)}\).
Special Cases & Applications:
Equilateral Triangle: While you can use the standard method by dropping a perpendicular line and using Pythagoras' theorem to find the height, Heron's formula simplifies to:
\(\text{Area} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}a^2\)
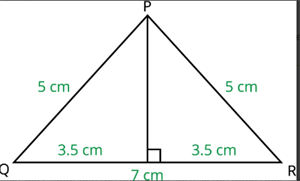
Isosceles Triangle: Similar to equilateral triangles, you can find the height using Pythagoras' theorem or apply Heron's formula directly using the two equal sides and the base.
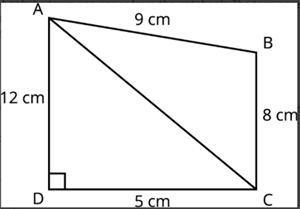
Quadrilaterals: To find the area of a quadrilateral, divide it into two triangles by drawing a diagonal. Calculate the area of each triangle (using Heron's formula or Pythagoras if a right angle is present) and add them together.
Important!
Heron's formula is universal; it can be applied to any type of triangle regardless of its angles or side lengths.