Right Circular Cylinder

It has two parallel circular bases and one curved surface. The axis joining the centers of the bases is perpendicular to the base planes.

Right Circular Cone:

It has one circular base and one apex. The line from the apex to the center of the base is the height \(h\).
Oblique Cone: A cone where the apex is not aligned directly above the center of the base.

Sphere and Hemisphere
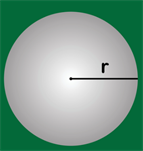
Sphere: A perfectly round 3D object where every point on the surface is equidistant \(r\) from the center. It is formed by rotating a semicircle around its diameter.
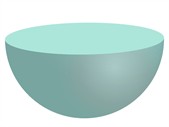
Hemisphere: Exactly half of a sphere. It has a curved surface and a flat circular top.
| Shape | Curved Surface Area (C.S.A.) | Total Surface Area (T.S.A.) | Volume (V) |
| Cylinder | \(2 \pi rh\) | \(2 \pi r(r+h)\) | \( \pi r^2h\) |
| Cone | \( \pi rl \) | \( \pi r(l+r)\) | \( \frac{1}{3} \pi r^2h\) |
| Sphere | \(4 \pi r^2\) | \(4 \pi r^2\) | \( \frac{4}{3} \pi r^3\) |
| Hemisphere | \(2 \pi r^2\) | \(3 \pi r^2 \) | \( \frac{2}{3} \pi r^3 \) |
Important!
Note:
- For a sphere, the Curved Surface Area and Total Surface Area are the same because it has no flat faces.
- The value of \(π\) should be taken as \( \frac{22}{7} \) unless its value shared in the problem