Set operation is an operation used to construct new sets from given sets.
There are several fundamental operations for constructing new sets from given sets. They are:
- Universal set.
- Union of two sets.
- Intersection of two sets.
- Difference of two sets.
- Symmetric difference of sets.
- Complement sets.
- Disjoint sets.
- Overlapping sets.
Universal set:
A universal set is the set of all elements under consideration, denoted by capital \(U\). All other sets are subsets of the universal set.
In the Venn diagram below, represents a universal set.

Union of two sets:
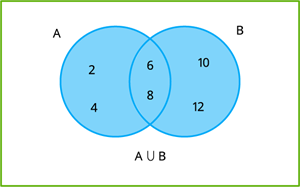
Let \(A\) and \(B\) be any two sets. The union of \(A\) and \(B\) is the set consists of all elements of \(A\) and \(B\); common elements being taken only once. The symbol \(∪\) is used to denote the union. Symbolically, we write \(A ∪ B\) and usually read as \(A\) union \(B\).
Symbolically, we write \(A\cup B = \{x: x\in A\ \mathrm{or}\ x\in B\}\)
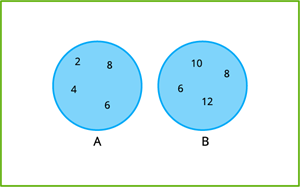
Let \(A=\{2,\ 4,\ 6,\ 8\}\) and \(B=\{6,\ 8,\ 10,\ 12\}\).
Then, \(A\cup B=\{2,\ 4,\ 6,\ 8,\ 10,\ 12\}\)
Note: Common elements \(6\) and \(8\) have been taken only once while writing \(A ∪ B\).
In the Venn diagram below \(A\) and \(B\) are represented.
In the Venn diagram below, the area in the blue colour represents \(A ∪ B\).
Intersection of two sets:
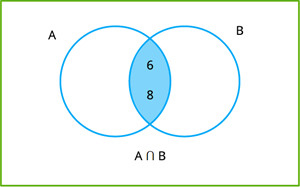
The intersection of sets \(A\) and \(B\) is the set of elements which are common in \(A\) and \(B\). The symbol \(∩\) is used to denote intersection.
Symbolically, we write \(A\cap B=\{x:x\in A\ \mathrm{and}\ x\in B\}\).
Numerical: Let \(A=\{2,\ 4,\ 6,\ 8\}\) and \(B=\{6,\ 8,\ 10,\ 12\}\).
Then, \(A\cap B=\{6,\ 8\}\).
In the Venn diagram below \(A\) and \(B\) are represented.

In the Venn diagram below, the area in the blue colour represents \(A ∩ B\).
Important!
The relation "is an element of", also called set membership, is denoted by the symbol "\(∈\)", and the relation "is not an element of", is denoted by the symbol "\(∉\)".