The straight wire is bent in the form of a circular loop, and a current is passed through it, as the magnetic field created by a current-carrying straight wire depends inversely on the distance from it.
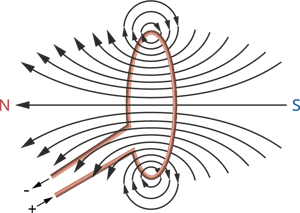
Magnetic field lines of the field produced by a current-carrying circular loop
Every point on the wire carrying current would give rise to the magnetic field appearing as straight lines at the centre of the loop.
Observations:
The magnitude of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying circular wire at its centre is:
- Directly proportional to the current passing through the circular wire.
\(B\ ∝\ I\), Where B - Magnitude of the magneticfield, I − Current
- Inversely proportional to the radius of the circular wire.
\(B\ ∝\ \frac{1}{r}\), Where B − Magnitude of the magneticfield r−Radius of the circular wire
- The strength of the magnetic field can be increased by taking a circular coil consisting of a number of turns of insulated copper wire closely wound together.
- If a circular coil has 'n' turns, the magnetic field produced by this current-carrying circular coil will be 'n' timesas large as that produced by a circular loop of a single turn of wire.
Solenoid:
A coil with number of circular turns of insulated copper wire covered closely in the shape of a cylinder is called a Solenoid.
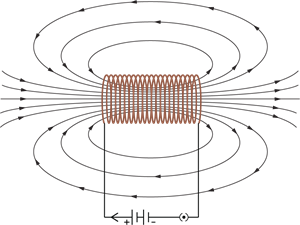
Field lines of the magnetic field through and around a current-carrying solenoid
The below figure shows the pattern of the magnetic field lines around a current-carrying solenoid. Pattern of the magnetic field produced by (a) Solenoid (b) Bar magnet. Yes, they are similar.
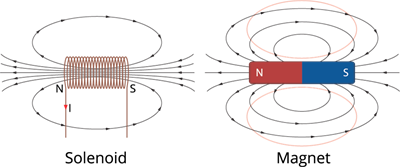
Magnetic field produced by (a) Solenoid (b) Bar magnet
One end of the solenoid functions as a north pole of the magnet, while the other is the south pole.
The magnetic field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines.
A strong magnetic field created inside a solenoid can be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material, like soft iron, when placed inside the coil. The magnet so formed is called an Electromagnet.
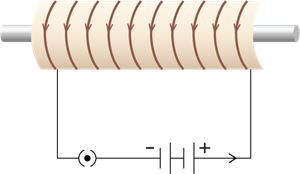
Current-carrying solenoid coil is used to magnetise the steel rod inside the coil
Increase magnetic field strength in a solenoid by,
- Increasing the current flowing through it,
- Increasing the number of turns on the coil per unit length,
- Inserting a soft iron core into the solenoid.
The following activity demonstrates the force due to a magnetic field acting on a current-carrying conductor.
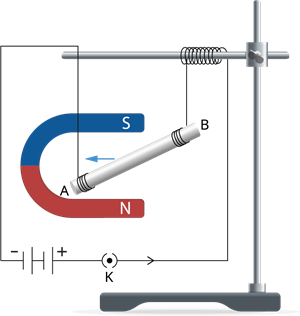
A current-carrying rod
It is seen that the rod is relocated towards the left. You will see that the rod gets relocated.
- Reverse the direction of current flowing through the rod (end A to B) and notice the direction of its displacement.
The rod is now relocated towards the right.
Fleming's left-hand rule:
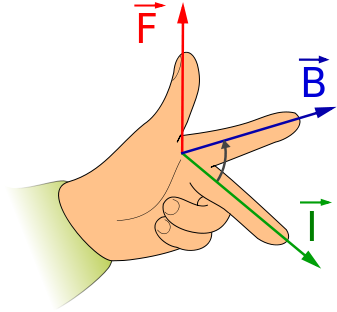
Fleming’s left-hand rule
According to Fleming's left-hand rule,
thumb, forefinger and middle finger of your left hand such that they are mutually perpendicular. first finger points - magnetic field direction
second finger - current direction,
thumb - direction of motion or the force acting on the conductor.
Fleming's left-hand rule shows the direction of the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
Domestic circuits:
In our homes, we receive a supply of electric power through the main supply (also called mains). One of the wires in this supply,
- red insulation - live wire (or positive)
- black insulation - neutral wire (or negative).
- green colour - earth wire.
Overloading can happen when the live wire and the neutral wire come into direct contact. In these situations, the current in the circuit suddenly increases. This is called short-circuiting.
The electric fuse prevents the electric circuit and the appliance from possible damage by preventing excessively high electric current flow. The Joule heating that takes place in the fuse melts it to break the electric circuit.
PYQ:
Exam tips:
- Concentrate on domestic circuits
- Hint words
- Diagram
- Arrow marks