Electricity:
Electricity is one form of energy involving the flow of electrons.
The nucleus includes,
- Protons - positively charged particles, and
- Neutrons - uncharged particles
The nucleus of an atom is enclosed by negatively charged particles known as electrons.
What could be the effects of electric current?
When current flows in a circuit, it shows various effects. The main effects are,
- Heating
- Chemical, and
- Magnetic effects
Electromagnetism:
In the 19th century, one of the leading scientist, Hans Christian Oersted, played an important role in understanding the concept of Electromagnetism.
In 1820, he accidentally found that a compass needle gets deflected when an electric current passed through a metallic wire placed nearby.
Through this observation, Oersted confirmed that electricity and magnetism were related phenomena. His research later produced technologies such as radio, television and fibre optics.
The unit of magnetic field strength is named after Oersted in his honour.
What is Electromagnetism?
Electromagnetism is a branch of physics. It deals with the study of electromagnetic force, a physical interaction between electrically charged particles.
The electromagnetic force is carried by electromagnetic fields comprised of electric and magnetic fields, responsible for electromagnetic radiation such as light.
The magnetic compass is a device that is used to locate the direction of a place.
It always rests in a north-south direction and is very helpful as a navigator in ships, submarines and aeroplanes.
A compass needle acts as a small bar magnet. we have observed that like poles repel, while unlike poles of magnets attract each other.
Working principle of Magnetic compass:
The magnetic compass works with the Earth’s magnetic field principle and shows the magnetic North and South. The magnetic compass has a magnetised needle, that can freely rotate in a horizontal plane. Such a magnetic needle tends to settle in the magnetic meridian.
What happens if we put a compass needle near a bar magnet?
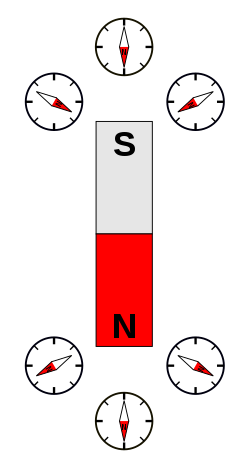
Deflection of compass when it is brought near a bar magnet
We can see that the red portion inside the bar magnet and the needle represents the North pole. And, the grey and white portions represent the bar magnet's South pole and the needle.
You can observe that the North pole in the magnetic needle is always deflected towards the South pole of the bar magnet and vice-versa.
Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
A compass needle gets deflected whenever a bar magnet is brought near to it. Because, a magnetic compass can be assumed as a pole, and the magnet creates a magnetic field.
If we place both a compass and the magnet at rest, the compass will be reflected in a direction and constant.
But if you move the magnet, it will alter the generated flux lines. Through this we can conclude that there is a change in direction or magnitude, and the needle gets deflected near a bar magnet.
We know that an electric current-carrying wire acts like a magnet.
Let us do the following activity to reinforce it.
Let us do the following activity to reinforce it.
Steps:
- Take a straight, thick copper wire and fix it between the point X and Y in an electric circuit, as shown in the below figure.
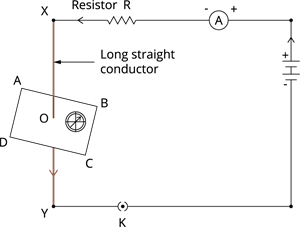
Electric circuit
- The wire XY is maintained perpendicular to the plane of the paper.
- Horizontally, place a small compass near this copper wire.
- Observe the position of its needle.
- Pass the current through the electric circuit inserting the key into the plug.
- Observe the change in the position of the compass needle.
Observation:
We observe that the needle is deflected.
What does it mean?
It means that the electric current flows through the copper wire have induced a magnetic effect.
Thus, we can state that electricity and magnetism are connected.