Refraction through glass slab:
Glass slab does not deviate, nor does it disperse the light rays whenever passing through it. This suggests that the incident and the emergent ray emerging from the glass slab are parallel. The glass slab only creates a lateral or sideways shift or displacement to the direction of light.
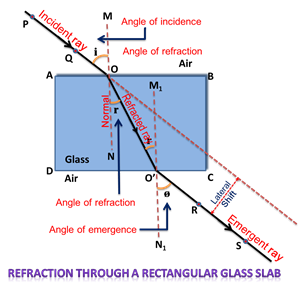
The refraction happens only at the boundary. Once the light has passed the boundary between the two media, it travels in a straight line.
The relative speed of light propagation in different media can be linked to the refractive index, a significant physical quantity.
In a vacuum, light travels at the fastest speed. When compared to vacuum, the speed of light in air is only slightly slower. In glass or water, it shrinks dramatically.
In a vacuum, light travels at the fastest speed. When compared to vacuum, the speed of light in air is only slightly slower. In glass or water, it shrinks dramatically.
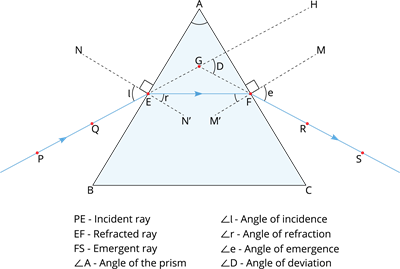
Refraction through glass prism:
The peculiar shape of the prism makes the emergent ray bend at an angle to the direction of the incident ray. This angle is called the angle of deviation.
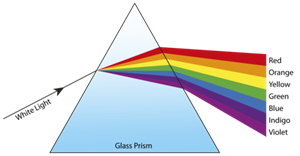
Dispersion:
- Turn the prism slowly until the light that comes out of it appears on a nearby screen
You will find a beautiful band of colours.
The prism has probably split the white incident light into a band of colours.
Observe the colours that appear at the two extremes of the colour band.
The different colours seen are Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red, as shown in the figure.
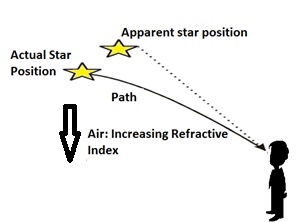
Atmospheric refraction:
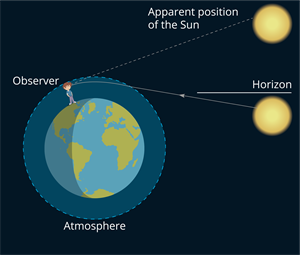
The twinkling of a star is because of the atmospheric refraction of starlight. On entering the earth's atmosphere, the starlight experiences refraction continuously before it reaches the earth. The atmospheric refraction happens in a medium of continuously changing refractive index. Since the starlight is bent by the atmosphere towards the normal, its apparent position is slightly different from its actual position.
Rainbow formation - refraction, dispersion, total internal reflection.
Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset:
Advanced Sunrise:
The sun is rising above the horizon during sunrise. The rays from the sun refract as they move from denser (more dense) air to lighter air. Also, the human eye can see the sun rays as a straight line, which appears as the sun has risen. But it has actually not yet risen.
The sun is rising above the horizon during sunrise. The rays from the sun refract as they move from denser (more dense) air to lighter air. Also, the human eye can see the sun rays as a straight line, which appears as the sun has risen. But it has actually not yet risen.
Delayed Sunset:
The sun, after sunset, is setting below the horizon. Now, the sun's apparent position is visible to us, not the actual position. This is because of the atmospheric refraction.
The sun, after sunset, is setting below the horizon. Now, the sun's apparent position is visible to us, not the actual position. This is because of the atmospheric refraction.
PYQ
Exam tips:
- Key words
- Understanding the question
- Diagram
- Arrow marks in diagram