A long time ago, a scientist named Galileo Galilei made an interesting discovery in a church. He saw a lamp hanging from the ceiling, swinging from side to side. He noticed that each swing took the same amount of time, even when the swing became smaller. He used his pulse to check the time.
Galileo then tried swinging different objects, called pendulums. He found that a pendulum of the same length always takes the same time to swing once. This is called one oscillation.
Later, in 1656, another scientist named Christiaan Huygens used this idea to make the first pendulum clock. This helped people measure time more accurately, leading to the clocks we use today.
The working of clocks are based on the concept of periodic motion.
Periodic motion:
The objects which are in repeated motion for equal intervals of time are in periodic motion. It is also known as oscillatory motion.
Example:
Girl swinging on a swing, motion of Earth around the Sun, the pendulum.
Simple Pendulum:
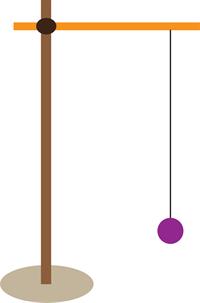
The simple pendulum consists of a metallic ball or a stone piece, a thread and a rigid stand. The metallic ball is generally called as the bob of the pendulum. Initially, in the mean position, the bob is at rest. The bob begins to move to and fro when the pendulum is released from one side, which is an example of a periodic or an oscillatory motion.
Working:
The bob starts from its mean position \(O\) goes to one end \(A\), then moves to the other end \(B\) and back to the point \(O\) in the middle. This to and fro motion is said to have completed one oscillation.
Time Period:
Time period is the time taken by the pendulum to complete one oscillation. Time period of a pendulum is constant.
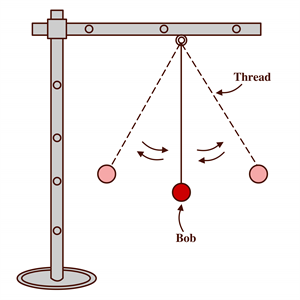
- Take a thread or a string of length \(1\) \(metre\) and fix it to the bob of the pendulum.
- Make the bob of the pendulum to be at rest in its mean position. This mean position of the bob is marked on the floor or wall.
- Now, hold the bob gently and move it to one side, to set it in motion. Note that the string should be in stretched position not in loose condition.
- The bob is now released and not pushed from its displaced position.
- A stopwatch, table clock or a wristwatch can be used to measure the time period of the pendulum. The time is noted when the bob is at its mean position or instead its extreme positions.
- When the pendulum completes \(10\) oscillations, the time is noted.
- This process is repeated again and the observations are made in the given table format.
Length of the string = \(1\) \(metre\)
| S.No | Time taken for \(10\) oscillations (\(s\)) | Time period (\(s\)) |
| 1. | \(20\) | \(2\) |
| 2. | \(40\) | \(4\) |
| 3. | \(60\) | \(6\) |
Calculation of time period of a pendulum:
- The time period or the time taken for one complete oscillation is calculated by dividing the \(10\) oscillations by \(10\).
\(\text{Time period} = \frac{\text{Time taken for 10 oscillation}}{\text{10 oscillations}}\)
- From this, it is observed that the time period of the pendulum is the same and it does not get affected by any change in the initial displacement.
- The time period of a simple pendulum of a given length is constant at a place and this is used in the measurement of time.
Time:
Time is measured in the units of second (\(s\)), minute (\(min\)) and hour (\(h\)). The larger units of time are minutes (\(min\)) and hours (\(h\)) whereas second (\(s\)) is a smaller unit.
The SI unit of time is the second. Its symbol is \(s\).
Important!
- Units of time like second, minute, and hour should always begin with a lowercase letter, unless they appear at the start of a sentence.
- Their symbols , ‘\(s\)’ for second, ‘\(min\)’ for minute, and ‘\(h\)’ for hour are also written in lowercase and always in singular form.
- Do not place a full stop after these symbols unless it ends the sentence.
- When writing time, make sure to leave a space between the number and the unit. For example: 45 \(s\). Avoid using incorrect forms like ‘sec’ for second or ‘hrs’ for hour.
Example:
- Age is generally expressed in years and not in days or hours.
- The time taken to travel between two places is expressed in days or hours and not in years.
- It takes around one second to spell 'one thousand and one' aloud.
- The pulse of a human heart beats about 72 times in a minute.
The time period between two sunrises is called a day.
1 day=24 hours
Likewise, the time interval between one new moon to the next new moon was called as a month.
1 month=30 days
The time taken by the Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun is known as a year.
1 year=365 days
1 year=366 days (For leap year)