After the funfair, Aaron and Andy were travelling back home with their father. Andy looked into the rear-view mirror and said, "Dad, the cars behind us look so small, but they seem to grow bigger as they come closer!"
His Dad smiled and replied, “That’s because the rear-view mirror is a convex mirror. It makes things look smaller but helps us see a wider view of the road.”
Aaron asked, “So, do all curved mirrors do that?”
“No,” said Dad. “Some mirrors, like concave mirrors, make objects look bigger.
Let us perform an activity to understand the images formed by concave and convex mirrors.
Activity:
To understand the difference in images formed by concave and convex mirrors.

Concave mirror
Step 1: Place both the concave and convex mirrors side by side in an upright position.
Step 2: Light a candle and place it in front of both mirrors at a small distance of about 4-5 cm.
Step 3: Observe the images of the candle formed in each mirror and note whether the images are erect or inverted, smaller or larger.
Step 4: Now slowly move the candle farther away from the mirrors and observe how the images change in each mirror.
Step 5: Repeat the above steps with each mirror separately to observe their individual behavior.

Convex mirror
Observation:
The concave mirror forms an erect and enlarged image when the candle is close to it, but as the candle is moved farther away, the image becomes inverted and smaller.
The convex mirror always forms an erect and diminished image, which becomes slightly smaller as the candle is moved farther away.
Conclusion:
Concave mirror: Can form both real and virtual images, sometimes inverted, sometimes erect.
Convex mirror: Always forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image.
Comparison of images formed by different mirrors:
| Type of mirror | Position of object | Orientation | Size of image |
|
Concave mirror
|
Close to the mirror | Erect (upright) | Enlarged |
| Concave mirror | Far from the mirror | Inverted | Smaller as the object moves away |
| Convex mirror | Close to the mirror | Erect (upright) | Smaller |
| Convex mirrror | Far from the mirror | Erect (upright) | Much smaller, size decreases slightly as the object moves away |
| Plane mirror | Any position | Erect (upright) | Same size |
The common characteristic of all the three mirrors is the lateral inversion.
Lateral inversion:
Lateral inversion is the phenomenon in which the left side of an object appears as the right side and the right side appears as the left side in its mirror image.
Uses of concave mirrors:
1. Torches and vehicle headlights:
- The reflectors are concave in shape.
- They focus light into a strong, bright beam.

Torch light
2. Dentist’s mirror:
- Provides an enlarged view of teeth when held close to the mouth.
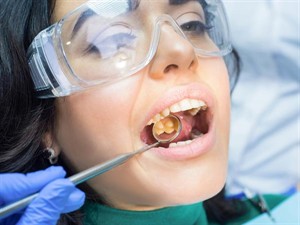
Dentist's mirror
3. Telescopes:
- Most modern reflecting telescopes use concave mirrors as the main mirror.
- They gather and focus light from distant objects like stars and planets.

Telescopes
Uses of convex mirrors:
1. Vehicle side-view mirrors:
- Always form erect and smaller (diminished) images.
- Provide a wider field of view of the road behind.

Car's side-view mirror
2. Road safety at intersections and sharp bends:
- Allow drivers to see traffic coming from the other side.
- Help prevent collisions.

Road safety mirror
3. Security in large stores:
- Monitor a large area to deter thefts.

Security mirror in store