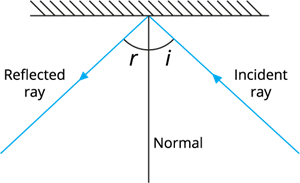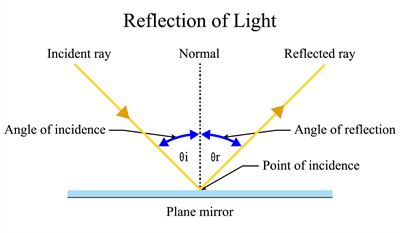
Reflection of light
Aaron and Andy leaned closer to the mirror, watching the light glint off its surface. “So, the same rules work for all mirrors like plane, concave, or convex?” asked Andy.
“Yes,” said their father. “No matter what kind of mirror it is, light always reflects in a definite way.”
Let us perform an activity to understand.
Activity:
To observe how parallel beams of light reflect from plane, concave, and convex mirrors.
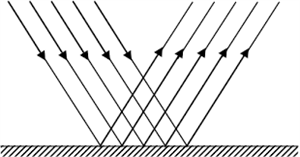
Plane mirror producing parallel beam
Step 1: Set up the mirrors one by one on their stands.
Step 2: Place the stencil upright in front of the torch and fix it with a paper clip or holder.
Step 3: Switch on the torch so that light passes through the openings of the stencil, forming multiple parallel beams of light.
Step 4: Direct these parallel beams toward the plane mirror, concave mirror, and convex mirror, one after another.
Step 5: Observe how the reflected beams behave in each case.
Observations:
- From the plane mirror, the reflected beams remain parallel.
- From the concave mirror, the reflected beams come closer together, they converge.
- From the convex mirror, the reflected beams spread out, they diverge.
Conclusion:
Even though each light ray follows the laws of reflection, the shape of the mirror affects how the reflected beams behave, a concave mirror makes them converge, a convex mirror makes them diverge, and a plane mirror reflects them parallel to each other.
Convergence:
- When light rays come together or meet at a single point after reflection, it is called convergence.
- A concave mirror causes parallel rays of light to converge at a point called the focus. It is also known as converging mirror.
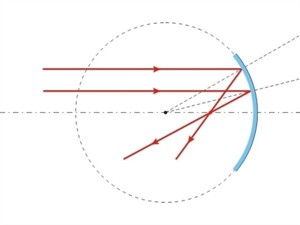
Concave mirror
Divergence:
- When light rays spread out or move away from a single point after reflection, it is called divergence.
- A convex mirror causes parallel rays of light to diverge after reflection. It is also known as diverging mirror.
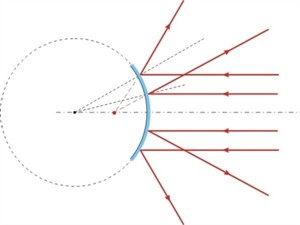
Convex mirror
As Andy shone a torch on the concave mirror, he noticed the light rays coming together at one point.
“Dad,” he asked, “since the concave mirror brings light together, does it make the light focus on a small area?”
“Yes,” said Dad. “A concave mirror converges light rays, concentrating them at a single point called the focus.”
“Dad,” he asked, “since the concave mirror brings light together, does it make the light focus on a small area?”
“Yes,” said Dad. “A concave mirror converges light rays, concentrating them at a single point called the focus.”
Let us understand with an activity.
Activity:
To show that a concave mirror converges sunlight to a point.
To show that a concave mirror converges sunlight to a point.
Important!
Caution: This activity should be performed under adult supervision.
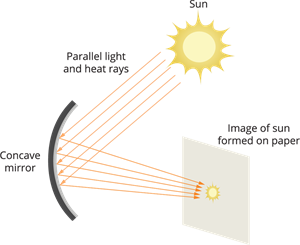
Concave mirror concentrating sunlight
Step 1: Hold the concave mirror with its reflecting surface facing the Sun.
Step 2: Allow the sunlight reflected from the mirror to fall on the sheet of paper.
Step 3: Adjust the distance between the mirror and the paper until you see a small, bright spot of light on the paper.
Step 4: Keep the mirror and the paper steady for a few minutes.
Observation:
After a short time, the paper begins to smoke or burn at the point where the bright spot appears.
After a short time, the paper begins to smoke or burn at the point where the bright spot appears.
Conclusion:
The concave mirror converges sunlight to a single point called the focus, where the light energy gets concentrated and produces enough heat to ignite the paper.
The concave mirror converges sunlight to a single point called the focus, where the light energy gets concentrated and produces enough heat to ignite the paper.
Important!
Devices that use mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight onto a small area are called solar concentrators. They concentrate sunlight to heat a liquid, which produces steam. This steam can then be used to generate electricity or provide heat for various purposes, such as large-scale cooking or in solar furnaces.
In fact, solar furnaces can become so hot that they are even used to melt steel!
In fact, solar furnaces can become so hot that they are even used to melt steel!