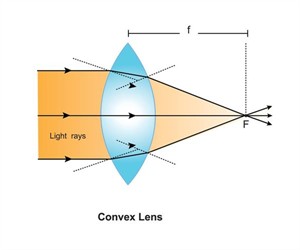
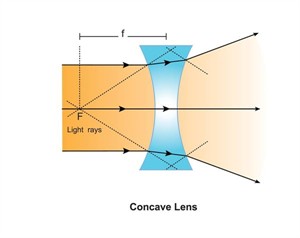
Step 1: Place a thin glass plate, convex lens and a concave lens upright on a table.
Step 2: Use a torch and a stencil to get parallel beams of light.
Step 3: Direct the light beams onto the lenses and observe how they pass through.
Step 4: Note whether the rays meet at a point or spread out.