Importance of heat in combustion:
Air is essential for the process of burning, but is it the only requirement for combustion? A paper is a combustible material; when it is kept surrounded by air, even for a long time, it will not catch fire.

Burning of LPG
What else is needed for the paper to burn?
The source of heat is essential for combustion to start. The gas stove does not start burning even if there is fuel (LPG) and air (oxygen); it only starts to burn when an external source of heat ignites it.
Activity: To demonstrate that heat is essential for combustion
Materials required:
- A magnifying lens
- A dry paper
Instructions:
Step 1: Prefer a hot day, go to an open area where direct sunlight falls. Place the dry paper on a flat surface.
Step 2: Hold the magnifying lens so that sunlight falling on the paper appears as a bright point of light.
Step 3: The focus point should be the same; hold it steady for a few minutes. The directed sunlight will begin to heat the paper. Eventually, the paper begins to turn brown and catch fire.
Explanation: The sunlight produces heat source, and the magnifying lens focuses the light rays into a single point, thereby increasing the temperature of the paper. Once the paper reaches its ignition temperature, it begins to burn.
Physical and chemical changes occuring in the same process:
Indeed, both physical and chemical changes can take place simultaneously in the same process. It occurs when a process includes alterations in physical properties (such as form, state, or size) and changes in chemical properties (resulting in the formation of new substances).
The burning candle undergoes both physical and chemical changes. A physical change influences the look or shape, whereas a chemical change modifies the substance itself.
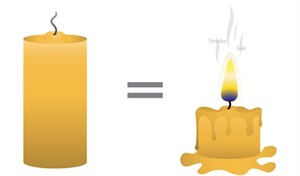
Burning of a candle
i. As the candle heats up, the hard wax begins to transform into liquid. This transformation is similar to the candle changing its appearance; it looks different (from solid to liquid), yet it remains the same wax. There is no formation of a new substance, and this is an example of physical change.
ii. The wick of the candle ignites and starts to consume the wax vapour. The wax interacts with oxygen in the air, transforming into carbon dioxide and water vapour and resulting in the formation of a new substance, and this is a chemical change.
Hence, on lighting the wick, the candle starts to melt because it absorbs heat from the wick (chemical change), making the candle wax melt (physical change).
Reversible change:
A reversible change refers to a transformation that returns to its original substance or condition. There is no formation of a new substance. Typically involves physical changes.
The reversible changes, which allow the objects to return to its original shape and size, are reversible.
Example:
Freezing of water, melting of ice, stretching of a rubber band, blowing a balloon, and folding a paper.


Blowing a balloon
Blow a balloon in such a way that it does not burst. There is a change in the shape and size of the balloon when air blows into it. Now, when the air is allowed to escape from the balloon, it turns to its original shape and size.

Making paper cup
Making a toy ship by folding a sheet of paper. When we unfold the paper again, it comes to its original shape.

Making shapes with dough
Likewise, dough is made into a ball and rolled out into a roti. If its shape is not good, it can be changed back into a ball of dough again.
In all the above examples, the substance changes into its original shape and size.
In all the above examples, the substance changes into its original shape and size.
Irreversible change:
An irreversible change refers to a transformation that is irreversible, resulting in the formation of a new substance. Unable to revert to the initial state. Frequently involves chemical transformations.
The changes are irreversible, preventing them from reverting to their original shape and size, and are termed irreversible changes.
Example:
Burning of a candle, rusting of iron, burning of paper
This type of change is permanent and cannot be undone by any means. A new substance is formed in this type of change.


Bursting a balloon
1. Bursting a balloon: If a balloon is blown to its full size and pricked with the pointed tip of a pencil or needle, it cannot regain its original form.
2. Cutting a paper: On a sheet of paper, the shape of an aeroplane is drawn and cut along its outline.
2. Cutting a paper: On a sheet of paper, the shape of an aeroplane is drawn and cut along its outline.
3. Baking a roti: While making roti from dough, bringing back the dough from the roti is not possible. The change is irreversible.


Baking a roti
4. Pot making: A potter makes a pot using a lump of clay, and then forms it again into a lump, which is a reversible process. But when the same pot is baked in an oven, it cannot be shaped into a lump of clay again. So, this process becomes irreversible.


Pot making