A polynomial is an expression consisting of variables and coefficients that involves operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents.
Example:
\(x^2+6x\)
Here, the terms \(x^2\) and \(6x\) are connected by the addition operation, and exponents of the variable \(x\) are whole numbers.
Thus, the expression \(x^2+6x\) is a polynomial expression.
Consider a polynomial in one variable(\(x\)).
\(p(x) =\) \(a_{n}x^{n}\)\(+\)\(a_{n-1}x^{n-1}\)\(+...\)\(a_{2}x^{2}\)\(+\)\(a_{1}x\)\(+a_{0}\)
The terms of the polynomial are , , ..., .
The coefficient of the polynomial is , , …, , of the variable , , ..., , respectively
Example:
Consider the polynomial .
The terms of the polynomial are , , .
The coefficient of \(x^{2}\) is \(a\).
The coefficient of \(x\) is \(-8\).
The coefficient of \(x^{0}\) constant is \(9\).
If \(p(x)\) is a polynomial in \(x\) , the highest power of \(x\) in \(p(x)\) is called the degree of the polynomial \(p(x)\) .
Example:
\(p(x) = 9x^3 - 3x^2 +8x -2\).
The highest power of the polynomial \(p(x)\) is \(3\).
Therefore, the degree of \(p(x)\) is \(3\).
Polynomial classification based on degree:
Linear polynomial: A polynomial of degree \(1\): \(p(x) = 8x -2\)
Quadratic polynomial: A polynomial of degree \(2\): \(p(x) = 3x^2 +8x-2\)
Cubic polynomial: A polynomial of degree \(3\): \(p(x) = 9x^3-3x^2 +8x-2\)
Polynomial classification based on term:
A polynomial of one term is defined as a monomial: \(p(x)=8x\).
The two terms are referred to as binomial: \(p(x)=9x^3+3\).
And the three terms are referred to as trinomial: \(p(x)=7x^4+3x^3+7\).
The value of the polynomial \(p(x)\) at \(x=a\) is \(p(a)\) acquired when \(x\) is replaced by \(a\) (\(a∈R\)).
Example:
Write the value of \(p(x) = x^2+2x-1\) at \(x = 3\).
The value of \(p(x)\) at \(x = 3\) can be obtained by substituting the point \(x = 3\) in the polynomial.
Substitute \(x=3\) in the polynomial \(p(x)\).
\(p(3) = \)\(3^2+2(3)-1\)
\(=9+6-1\)
\(=14\).
Zero of polynomial p(x) is a real number '\(a\)' such that \(p(a)=0\).
Example:
Find the zero of the polynomial \(p(x)=3a\)
Putting \(p(x) = 0\) in the polynomial equation.
\(0 = 3a\)
Thus, \(a = 0\) is the zero of the polynomial \(p(x)=3a\).
Factor Theorem: If \(p(x)\) is a polynomial of degree \(n>1\) and \(a\) is any real number, then:
(i) \(x - a\) is a factor of \(p(x)\) , if \(p(a)= 0\) , and
(ii) \(p(a)= 0\) , if \(x - a\) is a factor of \(p(x)\).
This is an extension to the remainder theorem where the remainder is \(0\), which is \(p(a)=0\).
The graph of the polynomial of \(n\) degree intersects \(x -\) axis at atmost \(n\) points.
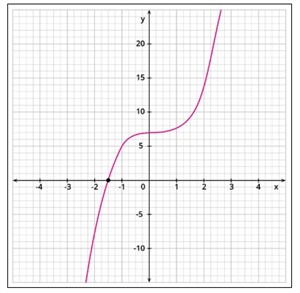
Here, the graph of the polynomial cuts the \(x-\) axis at one point.
Therefore, the number of zeroes of the polynomial is \(1\).