Prime and Co-prime:
A number that has only two factors is called a prime number. In other words, the numbers other than \(1\) whose only factors are \(1\) and the number itself are called prime numbers.
Example:
\(5 = 1\times 5\); \(23 = 1\times 23\).
Important!
Co-prime numbers, also known as relatively prime numbers are pairs of numbers that have no common factors other than \(1\).
Prime Factorisation:
Every composite number can be expressed (factorised) as a product of primes, and this factorisation is unique, apart from the order in which the prime factors occur.
Example:
Consider a composite number \(26950\).
Let us factor this number using the factor tree method.
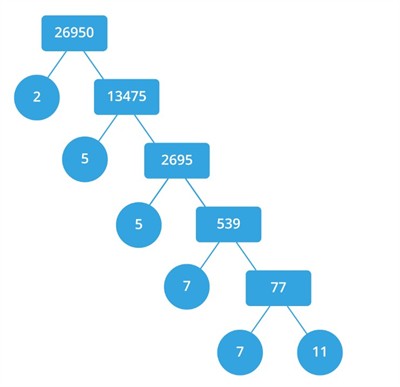
The prime factor of \(26950\) \(=\) \(2 \times 5 \times 5 \times 7 \times 7 \times 11\).
That is, \(26950 = 2 \times 5^2 \times 7^2 \times 11\).
Here, a composite number \(26950\) is written as a product of prime numbers.
If we change the order of the prime numbers, then also the answer will be the same composite number.
We can write \(26950 = 2 \times 7^2 \times 5^2 \times 11\) or \(26950 = 11 \times 7^2 \times 5^2 \times 2\).
Thus, the prime factorisation of a natural number is unique, except for the order of its factors.
HCF and LCM:
The Highest Common Factor (HCF) is the product of the smallest power of each common prime factor in the numbers.
Example:
Find the HCF of \(12\), \(18\) and \(24\).
Prime factors of \(12\) \(=\) \(2 \times 2 \times 3\).
Prime factors of \(18\) \(=\) \(2 \times 3 \times 3\).
Prime factors of \(24\) \(=\) \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3\).
HCF of \(12\), \(18\) and \(24\) \(=\) \(2^1 \times 3^1 =6\)
Therefore, HCF of \(12\), \(18\) and \(24\) is \(6\).
The Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) is the product of greatest power of each prime factor involved in the numbers.
Example:
Find the LCM of \(8\), \(15\) and \(24\).
Prime factors of \(8\) \(=\) \(2 \times 2 \times 2 = 2^3\).
Prime factors of \(15\) \(=\) \(3 \times 5 = 3^1 \times 5^1\).
Prime factors of \(24\) \(=\) \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 = 2^3 \times 3^1\).
LCM of \(8\), \(15\) and \(24\) \(=\) \(2^3 \times 3^1 \times 5^1 =120\)
Therefore, LCM of \(8\), \(15\) and \(24\) is \(120\).
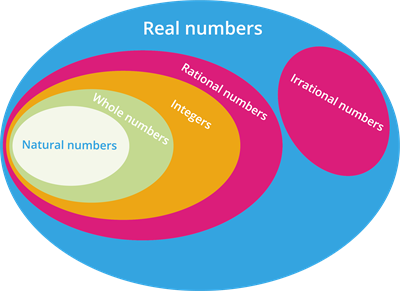
Rational and Irrational Number:
A number that can be expressed as \(a / b\), where \(a\) and \(b\) are integers and \(b ≠ 0\) is known as a rational number.
Example:
\(-2/3\), \(6/7\) and \(-3/1\) are rationals.
Irrational Numbers cannot be expressed in the form of \(p/q\), where \(p\) and \(q\) are integers and \(q ≠ 0\).
They are non-recurring, non-terminating, and non-repeating decimals.
Irrational numbers are real numbers but are different from rational numbers.
Example:
\(\sqrt{2}\), \(1.1121231.....\), \(1.618033....\) are some examples of irrational numbers.
Properties of Irrational Numbers:
- Addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of two irrational number is may or may not be irrational.
- Addition of rational and irrational number is always irrational.
- Subtraction of rational and irrational number is always irrational.
- Multiplication of rational and irrational is always irrational.
- Division of rational and irrational is always irrational.