In a triangle \(△ KLM\) , the internal bisector of \(∠L\) and the external bisector of \(∠KMN\) meet at a point
\(V\).
Verify that \(∠LVM=\frac{1}{2}∠LKM\)
Verification:
For a triangle \(△ KLM\), produce \(LM\) to \(N\) and the bisectors of \(∠KLM\) and \(∠KMN\) meet at point \(V\).
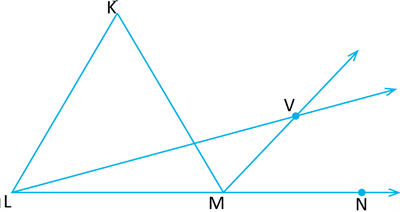
Now, \(MV\) is a bisector of \(∠KMN\)
Therefore, \(\frac{1}{2} ∠KMN=∠\) ------(a)
Also, \(BT\) is a bisector of \(△KLM\)
Therefore, \(∠MLV=\frac{1}{2}∠\) ----- (b)
In \(△ KLM\), \(∠KMN\) is an exterior angle.
Therefore, \(∠KMN=∠ KLM+∠ \)
\(\frac{1}{2} ∠KMN=\frac{1}{2} ∠\)\(+\frac{1}{2} ∠ KLM\)
\(∠TCD=\frac{1}{2} ∠\)\(+\frac{1}{2} ∠ KLM\) ------(1)
Again, in \(△ LVM\),
\(∠VMN=∠LVM+∠\) (since, Exterior angle \(=\) sum of two opposite angles)
\(∠VMN=∠LVM+\frac{1}{2}∠\) ------(2) [From equation (b)]
From (1) and (2),
\(\frac{1}{2} ∠\)\(+\frac{1}{2} ∠ KLM=∠LVM+\frac{1}{2}∠\)
\(\frac{1}{2}∠ MKL=∠LVM\)
That is, \(\frac{1}{2}∠ LKM=∠LVM\).