
Answer variants:
\(\Delta CPD\)
\(PC\)
\(PD\)
\(CD\)
\(PB\)
diagonals
A rectangle \(ABCD\) has diagonals \(AC\) and \(BD\). A point \(P\) is chosen as a intersecting point of two daigoanls, such that \(\bigtriangleup APB\) is equilateral. Using this information, prove that \(∆CPD\) is also equilateral.
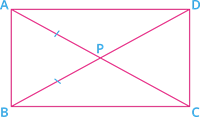
Proof:
Given: \(ABCD\) is a rectangle and diagonals intersect at \(P\).
\(\Rightarrow PA =\) \(= AB\) - - - - - - (II)
We know that, "the bisect each other".
\(PA =\) and \(PB = \) - - - - -- (III)
From (I), (II) and (III), we get that:
\(PA = PB =\) \(=\) \(= AB = CD\)
We obtained that in \(\Delta CPD\), \(PC = PD =\) .
Therefore, is an equilateral triangle.
We know that, "the bisect each other".
\(PA =\) and \(PB = \) - - - - -- (III)
From (I), (II) and (III), we get that:
\(PA = PB =\) \(=\) \(= AB = CD\)
We obtained that in \(\Delta CPD\), \(PC = PD =\) .
Therefore, is an equilateral triangle.